The difference between NMOS, PMOS and triode
Time:2024-05-17
Views:122
A MOS Transistor is a type of Field-Effect transistor (FET), whose name is derived from Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor. MOS tubes include two types: NMOS (N-Channel MOS) and PMOS (P-Channel MOS).
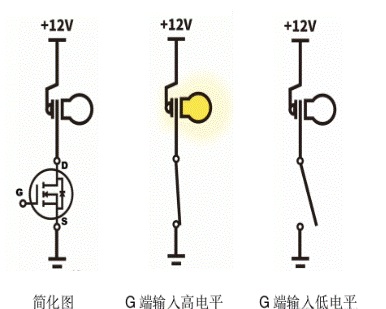

NMOS (N-Channel MOS) :
An NMOS tube is a type of field-effect transistor using an N-channel. It is composed of N-type channel, P-type base and control gate.
When a positive voltage is applied to the control gate, the resulting electric field causes electrons to flow in the N-type channel, thus conducting the NMOS tube.
The NMOS tube is characterized by a positive voltage applied to the control gate and a cut-off voltage applied to zero voltage.
PMOS (P-Channel MOS) :
A PMOS tube is a type of field-effect transistor using a P-channel. It is composed of P-type channel, N-type base and control gate.
When a negative voltage is applied to the control gate, the resulting electric field causes the holes in the P-channel to flow, thus conducting the PMOS tube.
The characteristics of the PMOS tube are that the control gate is switched on when negative voltage is applied, and the control gate is shut off when zero voltage is applied.
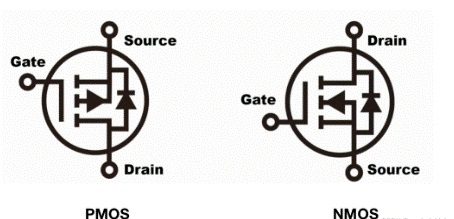
Difference between NMOS and PMOS

The difference between triode (bipolar transistor) :
A triode is a bipolar transistor with three control electrodes: emitter, base, and collector.
Unlike MOS tubes, triodes control the flow of current between the collector and emitter through the base current.
Triodes are widely used in amplification and switching circuits, while MOS tubes are mainly used in integrated circuits and digital logic circuits.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











