BLDC brushless DC motor FOC control technology solution
Time:2023-02-08
Views:1344
From the perspective of energy consumption, the transition of consumer electronics and industrial equipment from traditional AC motors to smaller and more efficient BLDC motors is of great significance. However, the complexity of designing BLDC control algorithms has hindered the enthusiasm of engineers to achieve this transition.

From small vibration motors in mobile phones to more complex motors used in household washing machines and air conditioners, motors have become daily devices in the field of consumption. Motor is also an important part of the industrial field, which is widely used in many applications, such as driving fans, pumps and other mechanical equipment. The energy consumption of these motors is huge: research shows that in China alone, the energy consumed by motors accounts for 60% to 70% of the total industrial energy consumption, and the energy consumed by fans and pumps accounts for nearly one quarter of the total power consumption in China. Although this figure may not be so high in other countries, reducing the motor energy consumption in electronic systems has become a priority issue in the world.
For more than a century, the traditional AC motor has been widely used. AC motors are the simplest induction motors in design, but they cause a lot of energy waste. This is because the AC motor only outputs a constant speed and cannot adapt to changes in working conditions. There are some simple methods to adjust the speed of AC motors (for example, standard household fans with three speed options), but these methods have limited application scope and are difficult to transfer to more complex systems.
However, for direct current (DC) motors, the speed can be changed and controlled by changing the voltage, so as to speed up or slow down the working speed according to the application needs. This can save a lot of energy, because the motor can operate according to the required conditions. In general, DC motor is more efficient than AC motor.
Figure 1: Replacing the traditional AC motor with a smaller and more efficient BLDC motor can save energy and reduce costs, but the algorithm required for BLDC control is so complex that many designers are unwilling to convert. The special IC specially designed for BLDC motor control can make this work easier.

Advantages of BLDC motor
The DC motor can be designed as a brush motor or a brushless motor. Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are usually the best choice for most applications. This kind of motor is more reliable, quieter, produces less electromagnetic radiation, and is safer, because they eliminate sparks caused by brushes and commutators. BLDC motors are smaller and more efficient, which means they need less energy.
The operating temperature of BLDC motor is lower than that of AC motor. The more efficient design makes its internal parts produce less heat. This can not only increase the service life of the bearing system, but also improve the reliability of the electrical system and the fan.
In addition, the power density of BLDC motor is also higher than that of AC motor. For the same energy output, the volume and weight of DC motor are smaller than that of AC motor. This makes the transportation and installation of BLDC motor easier and cheaper.
However, the trouble of using BLDC motor is that the system needs more complex electronic equipment to manage the motor. Motor control has not always been the focus of electronic engineers. Many developers cannot easily design the necessary control circuit because of lack of experience or professional knowledge. The research and development of BLDC motor requires additional time and technical support, which means longer development cycle and higher system cost, which makes it more difficult for system manufacturers to transition from familiar AC motor to BLDC motor.
However, for more and more manufacturers, the complexity of using BLDC motors will not be offset by the increase in market demand for more energy-saving appliances. According to the IMS survey in 2011, about 40% of China‘s air conditioners use variable-frequency control BLDC motors. This situation is on the rise, and to some extent, it is helpful for the special circuit designed for BLDC motor control.
Sensorless magnetic field guidance control technology
The traditional method used to control the BLDC motor is the six-step process of driving the stator, which produces pulsation on the torque generated. The so-called "six-step square wave" process uses Hall effect sensors to detect the permanent magnet position in the BLDC motor.
The six-step process is relatively simple, but it is easy to generate noise, and its response ability is insufficient for more advanced applications that need to quickly change the motor speed according to the change of conditions. Take the washing machine as an example, the load varies according to the selected washing cycle, and also varies during the whole cycle. In the drum washing machine, this situation is more complex. When the clothes rotate to the top of the drum, gravity will affect the motor.
In these cases, a more advanced algorithm is needed. Field-oriented control (FOC) can provide the response time required for rapid speed changes, and has become the choice of motor control methods for more advanced energy-saving appliances.
There are many ways to achieve FOC. One method is to use a sensor (similar to the six-step square wave process method), but the sensor is difficult to install and maintain, especially when the application involves complex wiring harness or the motor is exposed to water. The simpler and more cost-effective way to achieve FOC is to cancel the sensor. Sensorless FOC involves a constant rotor magnetic field generated by a permanent magnet on the rotor, which is a very effective control method.
FOC method can make the motor run smoothly in the full speed range, produce maximum torque at zero speed, and can accelerate and decelerate rapidly. In fact, due to the small size, low cost and power consumption of the motor, the advantages of sensorless FOC make it a popular choice in applications with low performance requirements.
Application-specific solutions
Even so, the implementation of sensorless FOC requires complex mathematical algorithms, which may not be familiar to ordinary designers. In the past, designers often relied on complex digital signal processing (DSP) chips to realize sensorless FOC. Taking Infineon‘s FCM8531 as an example, it provides engineers with special solutions, making it easier to develop sensorless FOC applications.
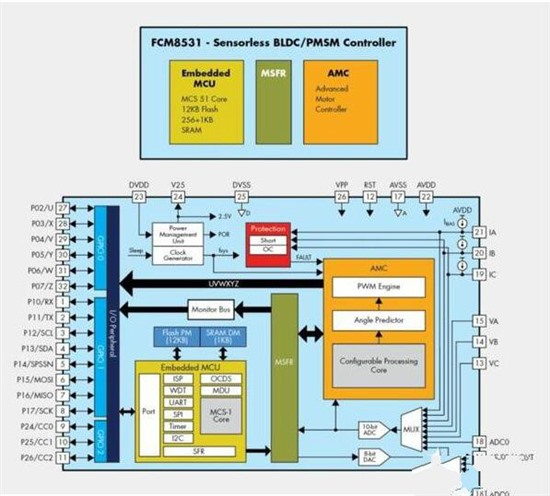
For systems using sensorless field-oriented control (FOC), Fast Semiconductor provides a specific application control device FCM8531 configured with a parallel core processor. As shown in Figure 1, FCM8531 consists of an advanced motor controller (AMC) processor and an 8-bit 80C51 compatible MCU processor.
Figure 2: FOC motor control IC function block diagram (taking FCM8531 as an example)

AMC is a core processor specially designed for motor control. It integrates a configurable processing core processor and peripheral circuits to perform sensorless FOC motor control. System control, user interface, communication interface and input/output interface can be programmed for different motor applications through embedded 80C51 MCU.
The advantage of the parallel core processor of FCM8531 is that the two processors can work independently and complement each other. AMC processes tasks specifically used for motor control, such as motor control algorithm, PWM control, current detection, real-time overcurrent protection and motor angle calculation. Embedded MCU provides motor control commands to AMC through communication interface to execute motor control activities. The complex motor control algorithm is implemented in AMC, so this method can reduce the software burden and simplify the control system program.
We provide users with motor control development system (MCDS) IDE and MCDS programming tools that can be used to develop software, compile programs and conduct real-time debugging. Designers can select the appropriate function from the function library and quickly compile the program control function and communication protocol to achieve the effect that can only be achieved on high-level DSP before.
conclusion
From the perspective of energy consumption, the transition of consumer electronics and industrial equipment from traditional AC motors to smaller and more efficient BLDC motors is of great significance. However, the complexity of designing BLDC control algorithms has hindered the enthusiasm of engineers to achieve this transition. The special IC specially designed for BLDC motor control, such as the FCM8531 of Fast Semiconductor, makes it easier for developers to use BLDC motor, and helps accelerate the transition and conversion to a more efficient mode.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











