The difference between inductive control and non-inductive control of brushless motor
Time:2024-06-07
Views:68
When BLDC performs trapezoidal wave control, the rotor magnetic pole position needs to be detected, and the stator coil is exchanged according to the detected position to form a 6-step rotating magnetic field, which drives the rotor to rotate synchronously. The detection of rotor magnetic pole position can be divided into motor with Hall sensor (inductive) and without Hall sensor method, the detection method of rotor magnetic pole position will be different, the direct BLDC control mode is different.
BLDC has sensory control
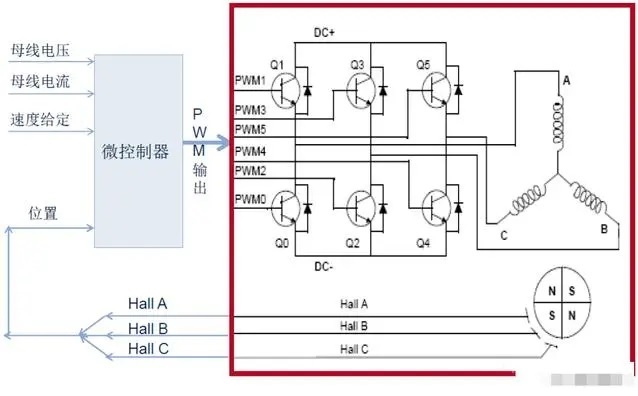
For BLDC inductive control, the BLDC motor itself is required to be equipped with a Hall sensor, and the motor hall sensor should be installed with a difference of 120°, as shown in the figure below.
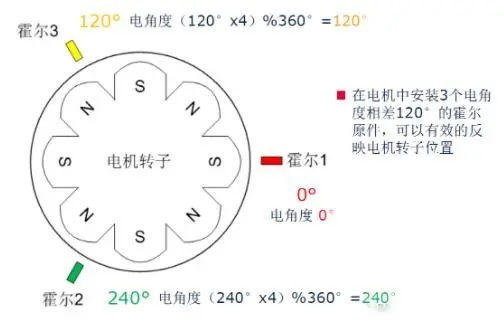
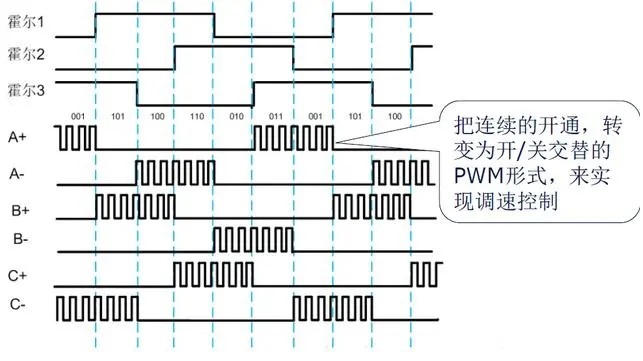
When the motor rotates in a certain direction, the output of the 3 halls will change according to the 6-step rule as follows:
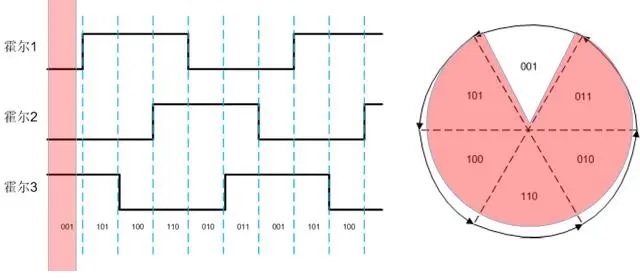
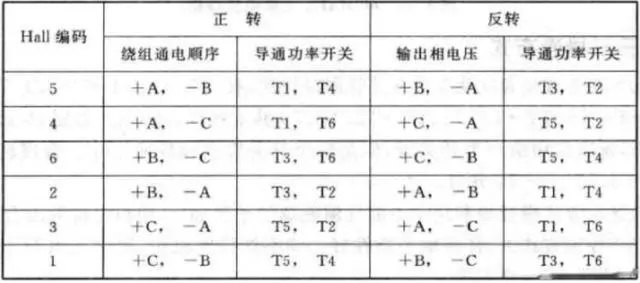
According to the position of Hall sensor, the three-phase winding is energized according to a certain law, so as to realize the control of the motor. Taking into account the different installation methods of each motor Hall sensor, the commutation switch table will have certain differences. The relationship can be determined according to the data provided by the manufacturer or the measured motor hall output.
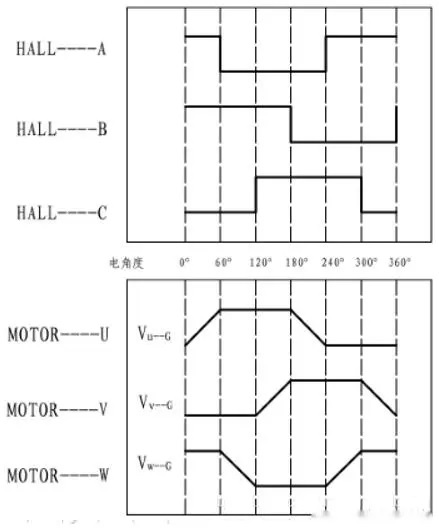
The following is the Hall output and back electromotive force output of A motor. It can be seen that when the Hall A output of the motor changes from 1 to 0, the control U+ is turned on.
The BLDC inductive control system is as follows:

BLDC Speed Control:
On the basis of BLDC electronic commutation, the equivalent output voltage can be changed by changing the PWM duty cycle during switching, so as to change the speed regulation.

BLDC non-inductive control

When using HALL sensors in BLDC, there are the following problems: HALL installation conditions are limited, Hall affects system reliability (Hall is easily damaged and needs to be repaired), Hall has requirements for installation accuracy, and there is a certain cost. Therefore, it is necessary to study the noninductive control method of BLDC.
The main task of BLDC sensorless control is to estimate the rotor position. The two basic techniques are as follows:
Technology based on back electromotive force induction: commutation based on back electromotive force zero crossing; The reverse electromotive force is required to be high enough and the speed range is 5-10% to 100% of the rated speed.
Technology based on salient pole of inductance of motor: based on transient current measurement; The speed range is from stationary to about 20% of the nominal speed.
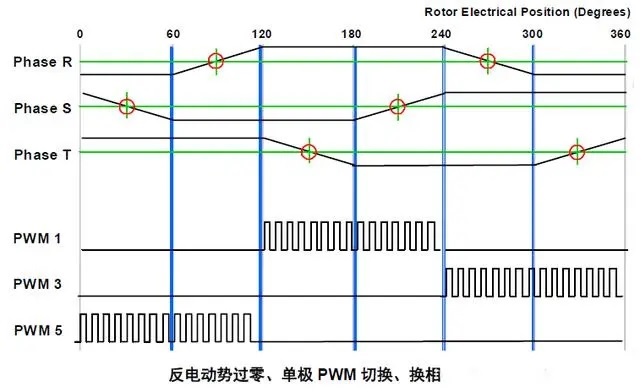
The method of zero crossing detection based on back electromotive force is commonly used, but it requires the motor to have a certain speed; It is sometimes used in combination, but requires the use of complex control algorithms. The following is mainly based on the back electromotive force induction technology is introduced.
The voltage waveform and back electromotive force waveform of the phase winding of the motor with correct commutation are shown in the figure. It can be seen from the figure that the correct commutation point should be delayed 30° at the zero crossing. Therefore, the back electromotive force zero crossing signal can be used as the calculation basis to estimate the correct commutation time point.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











