This section describes basic parameters of the lithium battery
Time:2024-05-21
Views:128
1. Capacity (unit: Ah)
This is one of the parameters that people care about. Battery capacity is one of the important performance indicators to measure battery performance, it indicates that under certain conditions (discharge rate, temperature, termination voltage, etc.) the battery released electricity (JS-150D can be used for discharge test), that is, the capacity of the battery, usually in ampere · hour unit (referred to as A·H, 1A·h=3600C). For example, a battery is 48V 200ah, then the battery can store 48V*200ah=9.6KWh, that is, 9.6 degrees of electricity. Battery capacity is divided into actual capacity, theoretical capacity and rated capacity according to different conditions.
Actual capacity refers to the amount of electricity that a battery can give under a certain discharge system (a certain sink, a certain current density and a termination voltage). The actual capacity is generally not equal to the rated capacity, which is directly related to temperature, humidity, charge and discharge ratio. Under normal circumstances, the actual capacity is smaller than the rated capacity, and sometimes even much smaller than the rated capacity;
Theoretical capacity refers to the amount of electricity given by all the active substances participating in the battery reaction. The optimal capacity;
Rated capacity refers to the capacity of the motor or electrical appliance indicated on the nameplate that can continue to work for a long time under rated working conditions. Usually the transformer refers to the apparent power, the motor refers to the active power, the phase modulation equipment refers to the apparent power or reactive power, the unit is VA, kVA, MVA;
In the application, the geometric size of the plate, the termination voltage, the temperature, the discharge rate, etc., will have an impact on the battery capacity, such as the northern winter, if the mobile phone is used outdoors, the battery capacity will decline rapidly.
2. Energy Density (unit: Wh/kg or Wh/L)
Energy density, battery energy density, the ratio of the energy that can be filled to the mass or volume of the energy storage medium for a given electrochemical energy storage device. The former is called "mass energy density", the latter is called "volume energy density", and the units are respectively watt · hour /kg Wh/kg, Watt · hour /L Wh/L. The electricity here is the integral of the capacity (Ah) mentioned above and the operating voltage (V). In application, energy density is more instructive than capacity.
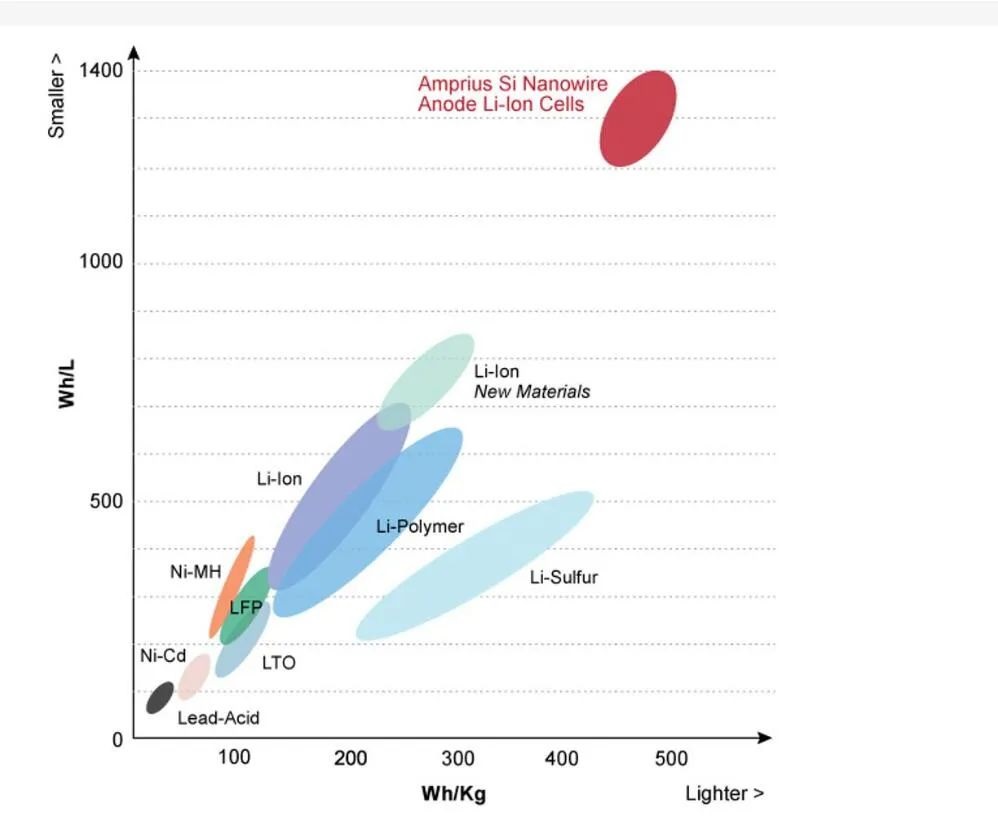

Based on the current lithium-ion battery technology, the energy density level that can be achieved is about 100~200Wh/kg, which is still relatively low, and has become the bottleneck of lithium-ion battery applications in many occasions. This problem also appears in the field of electric vehicles, in the case of volume and weight are strictly limited, the energy density of the battery determines the maximum single driving range of electric vehicles, so there is a unique term "mileage anxiety". If you want to make the single driving range of electric vehicles to reach 500 kilometers (comparable to traditional fuel vehicles), the energy density of the battery unit must reach more than 300Wh/kg.
The improvement of the energy density of lithium-ion batteries is a slow process, much lower than the Moore‘s Law of the integrated circuit industry, which causes a scissors gap between the performance improvement of electronic products and the energy density improvement of batteries, and it continues to expand over time.
3. Charge/Discharge rate (unit: C)
charge/discharge ratio is a measure of how quickly you charge. This indicator will affect the continuous current and peak current when the lithium-ion battery is working, and its unit is generally C(short for C-rate), such as 1/10C, 1/5C, 1C, 5C, 10C, etc. For example, the rated capacity of the battery is 20Ah, if its rated charge and discharge rate is 0.5C, then it means that the battery can be repeatedly charged and discharged with a current of 20Ah*0.5C=10A, until the cut-off voltage of charging or discharging. If its maximum discharge ratio is 10C@10s and maximum charge ratio is 5C@10s, then the battery can discharge at 200A for 10 seconds and charge at 100A for 10 seconds.


The more detailed the definition of charge and discharge ratio index, the greater the guiding significance for use. In particular, as a power source for electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries need to specify continuous and pulse rate indicators under different temperature conditions to ensure that lithium-ion batteries are used within a reasonable range.
4. Voltage (unit: V)
Lithium-ion battery voltage, open circuit voltage, working voltage, charging cut-off voltage, discharge cut-off voltage and other parameters


The open circuit voltage is that the battery is not connected to any load or power supply outside, and the potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of the battery is measured, which is the open circuit voltage of the battery.
Working voltage is the battery external load or power supply, in the working state, there is a current flowing, measured between the positive and negative electrode potential difference. The operating voltage is related to the circuit composition and the working state of the equipment, and is a variable value. Generally speaking, due to the existence of internal resistance of the battery, the working voltage in the discharge state is lower than the open circuit voltage, and the working voltage in the charging state is higher than the open circuit voltage.
Charge/discharge cutoff voltage refers to the maximum and minimum operating voltage allowed by the battery. Exceeding this limit value will cause some irreversible damage to the battery, resulting in reduced battery performance, and even cause fire, explosion and other safety accidents in serious cases.
5. Cycle Life (unit: times) and Depth of discharge (DoD)
The discharge depth is the percentage of the battery discharge to the rated capacity of the battery. The depth of discharge of shallow cycle batteries should not exceed 25%, and deep cycle batteries can release 80% of the electricity. The battery starts discharging at the upper limit voltage and terminates at the lower limit voltage. Define all of the discharged electricity as 100%. The battery standard 80%DOD means 80% of the charge. For example, the initial SOC is 100%, and I stop at 20%, which is 80%DOD.
The life of lithium-ion batteries will gradually decay with use and storage, and there will be a more obvious performance. Still taking smart phones as an example, after a period of time, the mobile phone can obviously feel that the mobile phone battery is "not durable", and it may only be charged once a day at the beginning, and it may need to be charged twice a day, which is the embodiment of the continuous decay of battery life.
The life of lithium-ion batteries is divided into two parameters: cycle life and calendar life. Cycle life is generally measured in number of times, indicating the number of times the battery can be charged and discharged. Of course, there are also conditions here, generally under the ideal temperature and humidity, with the rated charge and discharge current depth of charge and discharge (80%DOD), calculate the number of cycles experienced when the battery capacity decays to 20% of the rated capacity.


The definition of calendar life is more complex, the battery can not have been charged and discharged, there is storage and shelving, it can not have been in the ideal environmental conditions, will experience a variety of temperature and humidity conditions, charge and discharge rate is also changing at all times, so the actual service life needs to be simulated and tested. Simply put, the calendar life is the time span for the battery to reach the end of life conditions (such as capacity decay to 20%) under the use of environmental conditions and under specific use conditions. Calendar life and specific use requirements are closely combined, usually need to specify the specific use conditions, environmental conditions, storage intervals, etc.
Calendar life is more practical than cycle life, but because the calculation of calendar life is very complicated and takes too long, the general battery manufacturers only give the cycle life data. If you need to get data for the life of the calendar, you usually have to pay extra and wait a long time.
6. internal resistance (unit: Ω)
The internal resistance of lithium-ion batteries refers to the resistance of current flowing through the battery when the battery is working, which includes ohmic internal resistance and polarization internal resistance, and polarization internal resistance includes electrochemical polarization internal resistance and concentration polarization internal resistance.
Ohmic internal resistance is composed of electrode material, electrolyte, diaphragm resistance and contact resistance of each part. The internal resistance of polarization refers to the resistance caused by polarization in the electrochemical reaction, including the resistance caused by electrochemical polarization and concentration polarization.
The unit of internal resistance is generally milliohm (mΩ), the battery with large internal resistance, when charging and discharging, the internal power consumption is large, and the heat is serious, which will cause the accelerated aging and life attenuation of lithium-ion batteries, and will also limit the charging and discharging application of large rate. Therefore, the smaller the internal resistance, the better the life and rate performance of the lithium-ion battery will be.
7. Self-discharge
Self-discharge phenomenon is the phenomenon that if the battery is idle and not used, it will also lose power. When the battery is placed, its capacity is constantly decreasing, and the rate of capacity decline is called the self-discharge rate, which is usually expressed as a percentage: %/ month.
Self-discharge is what we do not want to see, a fully charged battery, put a few months, the power will be much less, so we hope that the self-discharge rate of lithium-ion batteries is as low as possible.
It needs special attention here that once the self-discharge of the lithium-ion battery causes the battery to overdischarge, the impact is usually irreversible, even if recharged, the available capacity of the battery will have a great loss, and the life will rapidly decay. Therefore, long-term placement of unused lithium-ion batteries, the battery must remember to charge regularly to avoid overdischarge due to self-discharge, and the performance is greatly affected.
8. Operating temperature range
Due to the characteristics of the internal chemical materials of lithium-ion batteries, lithium-ion batteries have a reasonable operating temperature range (common data between -20 ° C and 60 ° C), if it is used beyond a reasonable range, it will have a greater impact on the performance of lithium-ion batteries.
Different materials of lithium-ion batteries, its operating temperature range is not the same, some have good high temperature performance, some can adapt to low temperature conditions. The operating voltage, capacity, charge-discharge ratio and other parameters of lithium-ion batteries will change significantly with the change of temperature. Long time of high or low temperature use will also make the life of lithium-ion batteries accelerated decay. Therefore, efforts to create a suitable operating temperature range can maximize the performance of lithium-ion batteries.
In addition to the limitation of the operating temperature, the storage temperature of lithium-ion batteries is also strictly restricted, and long-term high or low temperature storage will cause irreversible effects on battery performance.7. Self-discharge
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











