What is a differential signal? Difference between differential signal and single-ended signal
Time:2024-05-19
Views:121
Differential transmission is a signal transmission technology, different from the traditional approach of one signal line and one ground line (single-ended signal), differential transmission transmits signals on both lines, and the amplitude of the two signals is equal and the phase is opposite.
 Compared with ordinary single-ended signal routing, the most obvious advantages of differential signals are reflected in the following three aspects:
Compared with ordinary single-ended signal routing, the most obvious advantages of differential signals are reflected in the following three aspects:


Strong anti-interference ability, because the coupling between the two differential lines is very good, when there is noise interference from the outside, it is almost coupled to the two lines at the same time, and the receiving end is only concerned about the difference between the two signals, so the common mode noise from the outside can be offset to the greatest extent.
Can effectively inhibit EMI, the same reason, because the polarity of the two signals is opposite, their external radiation electromagnetic field can cancel each other, the closer the coupling, the less electromagnetic energy released to the outside world.
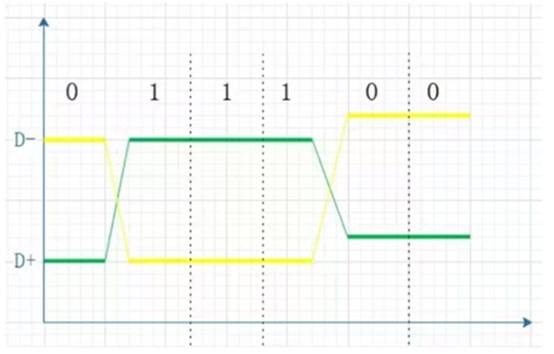
Timing positioning is accurate, because the switch change of the differential signal is located at the intersection of the two signals, unlike the ordinary single-ended signal depends on the high and low two threshold voltage judgment, so the influence of the process, temperature is small, can reduce the error on the timing, but also more suitable for low-amplitude signal circuit. The current popular LVDS refers to this small amplitude differential signal technology.
Difference between differential signal and single-ended signal
A single-ended signal is a signal transmitted by a wire. How can a wire have a signal without a reference point? The reference point is the ground. That is, the single-ended signal is the level difference between ground and transmitted on a pair of wires. So when you send A signal from point A to point B, the premise is that the ground potential at point A and point B should be about the same.

Differential signal refers to the signal transmitted by two wires, and the level difference between the two signals is transmitted. When you send A signal from point A to point B, the ground potential at point A and point B can be the same or different, but there is a range of ground potential differences between point A and point B, beyond which there will be problems.

A differential signal is a numerical representation of the difference between two physical quantities. Strictly speaking, all voltage signals are differential, because one voltage can only be relative to another voltage. In some systems, the system is used as a voltage reference point. When the local area is used as a reference for voltage measurement, this signal planning is called single-ended. We use the term because a signal is represented by a voltage across a single conductor.
On the other hand, a differential signal acts on two conductors. The signal value is the voltage difference between two conductors. The average of the two voltages will always be the same, though not necessarily. A differential signal is like two people on a seesaw. When one person is lifted off, the other person is lifted off - but their average position remains the same. Continuing the seesaw analogy, a positive value can mean that the person on the left is taller than the person on the right, while a negative value means that the person on the right is taller than the person on the left. 0 means that both people are at the same level. The two seesaws are represented by a pair of wires labeled V+ and V-. When V+ "V-", the signal is defined as a positive signal, and when V+ "V-", the signal is defined as a negative signal.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











