Design of Texas Instruments HD audio system
Time:2024-05-13
Views:121
In response to customer demand for top audio quality, audio system designers are looking into high-resolution or high-definition (HD) audio, as more and more mid-range system buyers demand the type of HD audio performance previously available only in high-end systems. In the past, the 44.1kHzCD quality sampling frequency was sufficient for most markets, but today (and for the foreseeable future), the demand for high-fidelity sound will only continue to grow.
According to professional and consumer audio equipment companies, higher sampling frequencies capture and reproduce a wider range of frequencies. Reproduction of audio frequencies greater than 20kHz, including ultra-high frequency harmonics, gives the characteristics of the subtle components of sound, especially acoustic instruments. According to these audio equipment companies, there are some technical advantages that make it worthwhile to move to higher sampling frequencies, such as the reduction of unwanted side effects due to the steep filters employed during digital-to-analog or analog-to-digital conversion.
Simply choosing an off-the-shelf music player will not deliver on the promise of high-resolution audio, which requires specialized hardware to truly enjoy its richness and subtleties. Of course, not every audio file or media is recorded in HD audio.
Design HD audio systems
As with every high-performance design, a whole-system approach to the entire audio signal chain ensures a robust and high-performance solution. Because every link in the audio signal chain is important, to ensure that it has no weakest link, each link must be able to meet all design target specifications such as performance, cost, time to market, and ease of use. Figure 1 shows the basics in an HD system.
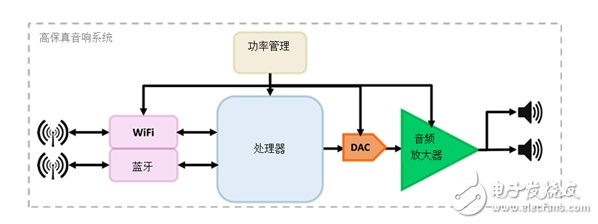

Figure 1: HD audio system
The power management module provides the correct power level for the Wi-Fi® speaker circuit. Assuming the application is system-powered (not battery-powered) and depends on the output power, the power supply not only needs to provide the voltage and current needed to meet the system‘s power requirements; It also needs to provide a clean and stable power rail to prevent any power noise from entering the audio system and degrading the audio quality.
The connectivity module provides wireless communication to the system using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth® via a computer, smartphone, tablet, or wireless-enabled product. Standard Bluetooth modules today provide an all-in-one solution for portable audio systems, as they themselves support both wireless and wired audio. But because lossless high-resolution audio streams require higher bandwidth, their limited bandwidth poses a potential bottleneck. The new Bluetooth audio coding technology promises increased bandwidth to support high-definition audio.
Wi-Fi, on the other hand, includes greater network capacity, powerful signaling, and a wider radio frequency range. Its increased bandwidth capacity and system throughput make it more suitable for HD audio applications.
The processor performs various audio processing functions, such as decoding and signal equalization, while also handling the Wi-Fi and/or Bluetooth communication software stack. In the past, the sampling frequency of CD quality may have been sufficient. But today‘s high-fidelity audio systems place other requirements on the processor in the signal chain, as high-fidelity sound quality requires sampling rates in the 48-khz to 192kHz range in a 24-bit music signal stream.
The audio module contains all the electronics needed to drive the speakers in the system. Because the signal from the connecting module and processor has low voltage and low current capabilities, the audio amplifier provides the signal with the higher voltage and current capabilities necessary to drive the driver in the speaker system. The module can include an audio digital-to-analog converter (DAC) for converting the digital audio signal from the processor into an analog audio signal, and provide other audio processing in the digital domain to further enrich the customer experience in high-end systems. Another key component of the audio module is the audio amplifier.
Audio amplifier: Class AB and Class D
When choosing the best audio amplifier for your HD audio system, you have two options: Class AB or Class D. Class AB audio amplifiers are linear amplifiers that do not require many external electronic components. But they are extremely inefficient and require a lot of passive or even active thermal management in the form of heat sinks and fans.
Class D audio amplifiers, on the other hand, are efficient switching amplifiers that require little thermal management, but they do require an output inductor.
For many years, the amplifiers in HD audio were Class AB amplifiers. Audio Class D amplifiers are considered non-compliant because they do not meet all the requirements for HD audio; It no longer exists. TI‘s latest generation of Class D amplifiers improves the overall performance and efficiency of HD audio systems by establishing a symbiotic relationship with the digital engine while efficiently transferring enhanced audio quality to the speakers.
Optimize HD audio design
High-performance HD audio amplifiers with integrated DAC and processing capabilities, such as TI‘s new TAS5782M, help audio designers greatly simplify designs, reduce costs and shorten design cycles. Integrated Dacs help reduce system complexity by providing a way to connect the audio amplifier directly to the processor, ensuring maximum signal integrity, and reducing the number of components.
Integrated audio processing can greatly help reduce the cost and compute requirements of the main application processor by offloading all audio processing into the amplifier itself. You can further reduce cost and size by reducing the cost and size of the main processor. Figure 2 is the optimized block diagram.
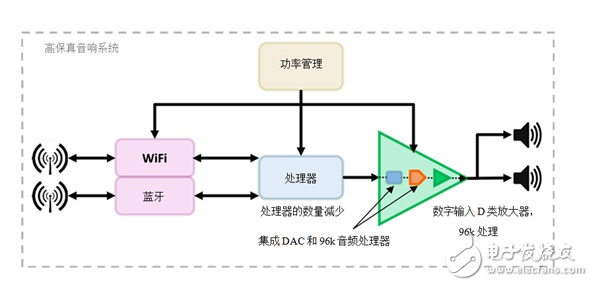
Figure 2: Optimized HD audio system
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











