One article provides a detailed explanation of light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
Time:2024-04-23
Views:149
D (Light Emitting Diode) is a semiconductor device that has the characteristic of converting electrical energy into light energy. The following is a detailed explanation of light-emitting diodes (LEDs):
1. Working principle:
LED is a type of diode that operates based on the electronic structure of semiconductor materials. When a forward voltage is applied to both ends of the LED, electrons flow from the N-type semiconductor to the P-type semiconductor, while holes flow from the P-type semiconductor to the N-type semiconductor. At the junction of two semiconductor materials, electrons and holes recombine and release energy, which is emitted in the form of light, producing visible light.
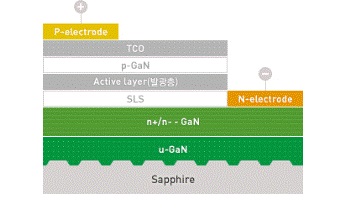

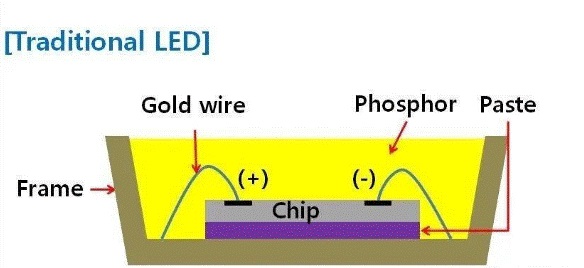
2. Structure:
The main components of LED include N-type semiconductor layer, P-type semiconductor layer, and active luminescent layer. The active luminescent layer is located between two semiconductor layers, and when current passes through the LED, it emits light within the active luminescent layer.

3. Characteristics:
High efficiency: LED has the characteristic of high efficiency. Compared to traditional light sources such as incandescent bulbs, LED can more effectively convert electrical energy into light energy, reducing energy waste.
Long lifespan: LEDs typically have a longer lifespan than traditional light sources, reaching tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of hours, and have a longer lifespan.
Quick response: LED has a very short response time and can quickly reach the predetermined brightness, suitable for applications that require quick switching.
Miniaturization: LED devices have a small volume and are easy to integrate into various electronic products, enabling compact design.
4. Type:
Conventional LED: emits monochromatic light, such as red, green, blue, etc.
Multicolor LED: By combining different LED chips, multiple colors of light can be emitted.
RGB LED: It includes three types of LED chips: red, green, and blue, and can generate rich colors by adjusting the brightness of each color.
High brightness LED: With high luminous brightness, it is suitable for situations that require high brightness light sources.
5. Application:
Lighting: LED is widely used in indoor lighting, outdoor lighting, and automotive lighting fields.
Display: LED is used for various display devices, such as LED display screens, digital displays, indicator lights, etc.
Indication and decoration: LED is used in various devices as indicator lights, decorative lights, car tail lights, etc.
Communication: LEDs can also be used in the field of optical communication, such as infrared LEDs for infrared remote controllers, etc.
Junction temperature of light-emitting diodes
The junction temperature of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) refers to the temperature inside the LED chip, which is the PN junction temperature of the LED chip. Junction temperature is one of the important factors affecting the stability and lifespan of LED operation. The typical junction temperature range of LED is usually between -40 ° C and+125 ° C, and different models of LED may have slightly different junction temperature characteristics.
The junction temperature of LED is influenced by various factors, including environmental temperature, LED current, LED packaging structure, etc. High ambient temperature and high current can cause an increase in the internal temperature of LED chips, thereby affecting the performance and lifespan of LEDs. Therefore, in LED design and application, it is usually necessary to consider heat dissipation measures to ensure that the junction temperature of the LED is within a safe range.


Luminescent intensity of light-emitting diodes
Luminous Intensity: The luminous intensity of a light-emitting diode can be measured by its luminous intensity, measured in candela (cd). Luminescence describes the light output intensity of an LED in a specific direction, usually perpendicular to the surface of the LED. The luminous brightness can be calculated by the luminous flux and luminous angle of the LED.
Radiant Power: This describes the total light output intensity of an LED in all directions, measured in watts (W) or milliwatts (mW). Luminescent power refers to the total amount of light energy generated by an LED, including visible light and infrared light.
Luminous Flux: Luminous flux is the total amount of light produced by an LED, measured in lumens (lm). The luminous flux considers the intensity of all visible light emitted by LEDs, rather than just the intensity in a specific direction.
Luminous Efficiency: Luminous efficiency describes the relationship between the light generated by an LED and the electrical energy consumed, typically expressed in lumens per watt (lm/W). The higher the luminous efficiency, the more effective LED can convert electrical energy into light energy.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











