The difference between IGCT and IGBT
Time:2023-11-28
Views:529
IGCT (Integrated Gate Converter Thyristor) and IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) are two semiconductor devices widely used in power electronics and power transmission systems. Although they have some similarities in functionality, they have unique features and applications.
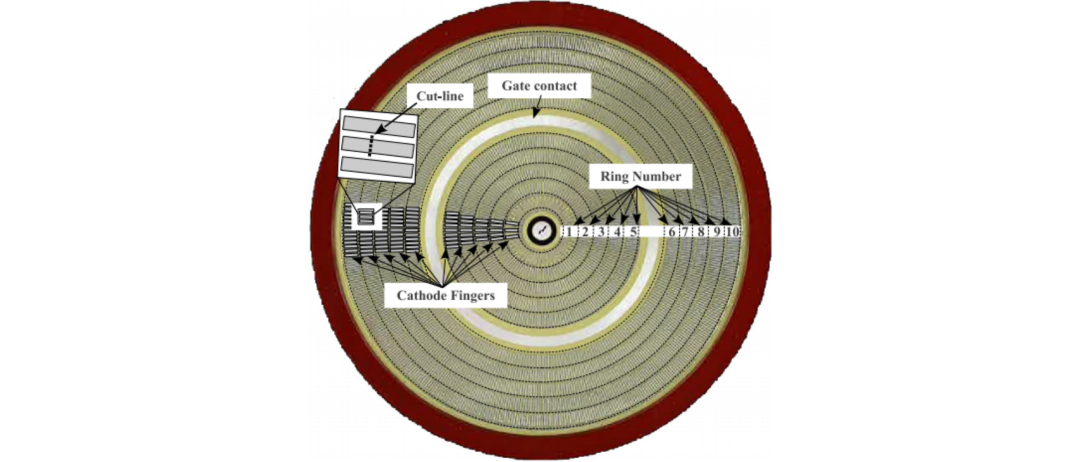
IGCT (Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor):
Meaning: IGCT is a type of thyristor that combines the characteristics of GTO (gate turnoff) thyristor and MOSFET (metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor). It integrates the advantages of these two devices, which can improve the overall efficiency and performance of high-power applications.

Features:
High power operation: IGCT is mainly used in managing high-power applications and can withstand high voltage and high current, making it suitable for various industrial and power transmission systems.
Turnoff capability: They have significant turnoff capability and can withstand large current surges, ensuring effective control and regulation of power flow within the system.
Durability: IGCT is renowned for its sturdy design and strong resistance to electrical stress and mechanical damage, ensuring reliable performance under harsh conditions.
Overcurrent and overvoltage protection: They are usually equipped with built-in protection functions, which have good reverse blocking ability, such as overcurrent and overvoltage protection, enhancing the overall safety and stability of the power system.
IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor):
Meaning: IGBT is a three terminal power semiconductor device that combines the properties of MOSFET and BJT (bipolar junction transistor). It is widely used in various electronic applications that require efficient power control and switching.
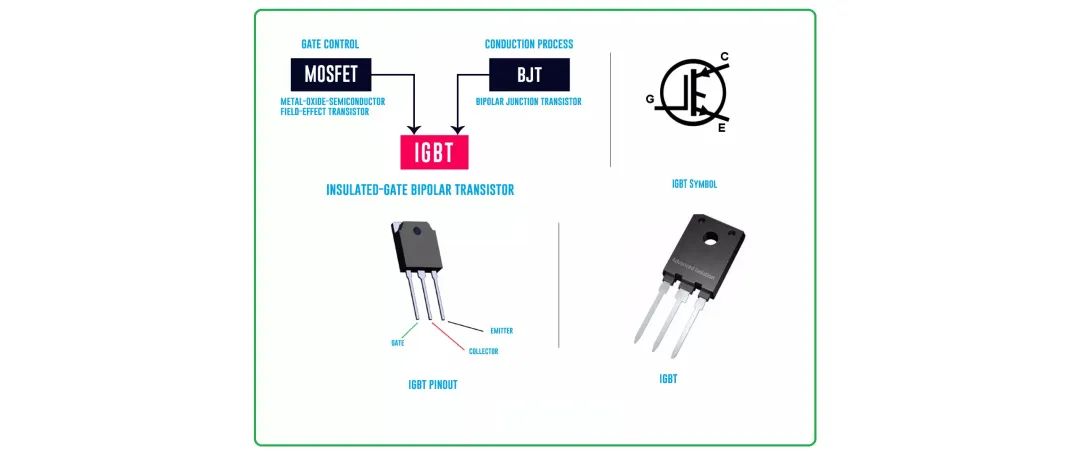

Features:
Voltage and current processing: The processing voltage is generally below 1200V, and they can manage various voltage and current levels, providing flexibility for various applications, including consumer electronics and industrial systems.
High switching speed: IGBT provides high-speed switching function, which is very suitable for applications that require fast switching and precise power control, such as motor drives and power supplies.
Efficiency: IGBT has lower conduction loss, therefore it has higher efficiency, which helps to save energy and reduce power loss in different power electronic systems.
External protection requirements: IGBTs typically require external protection circuits to ensure safe and reliable operation, especially in high-power applications.
A correct understanding of the differences between IGCT and IGBT is crucial for selecting appropriate devices for specific power management and control requirements, ensuring efficient and reliable operation of corresponding devices in various industrial and consumer electronics applications.
What is the difference between IGCT and IGBT?
IGCT (Integrated Gate Converter Thyristor) and IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) are semiconductor devices widely used in power electronics and power transmission. Although they have similar uses, they have significant differences in structure, characteristics, and applications.
Structure:
IGCT: IGBT is composed of an N-type metal oxide field-effect transistor (MOSFET) and a PNP type bipolar transistor (BJT), while IGCT is composed of two PNP type bipolar transistors. Therefore, the structure of IGCT is more complex and has a larger area.
Switching speed:
IGCT: The turn off and turn on times are slower. Their turn off time is relatively long, resulting in higher switching losses and limiting their use in high-frequency applications.
IGBT: With faster switching speed, it can operate efficiently at higher frequencies. This feature makes them suitable for high-frequency applications that require high-speed switching, such as motor drives, power supplies, and inverters.
Current and voltage:
IGCT: Typically used for high-power applications, it handles high currents and voltages and can withstand voltage levels of several thousand volts. They are commonly used in high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission systems, medium and high voltage distribution systems, and industrial power systems.
IGBT: Suitable for low-power and high-power applications, its rated voltage and current vary according to specific design and application requirements. The main application goal is to accurately control voltage batteries in some circuits in high-power environments. They are commonly used in consumer electronics, motor control, energy systems, and variable speed drives.
Protection and reliability:
IGCT: IGCT has built-in protection functions, including overcurrent and overvoltage protection, making it more robust and reliable in high-power applications.
IGBT: IGBTs require external protection circuits to ensure safe operation, as they are prone to malfunctions due to overcurrent, overvoltage, and overheating. However, the advancement of IGBT technology has led to the integration of various protection functions to improve their reliability.
Application:
IGCT: mainly used for high-power industrial applications, such as high-voltage transmission systems, static reactive power compensators (SVCs), and medium and high voltage motor drivers.
IGBT: Widely used in various applications, including motor drives, renewable energy systems (wind and solar), uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), electric vehicles, and household appliances.
IGCT and IGBT are both key components in power electronics, and their differences in structure, switching speed, current and voltage ratings, protection functions, and application areas make them different. These differences are crucial for selecting appropriate devices that are suitable for specific power control and conversion requirements.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











