Principle of three-phase brushless DC motor
Time:2023-10-11
Views:620
Principle of three-phase brushless DC motor
In order to achieve brushless commutation in a three-phase brushless motor, it is first required to place the armature winding of a general DC motor on the stator and the permanent magnet steel on the rotor, which is exactly the opposite of the structure of a traditional DC permanent magnet motor. The three-phase brushless motor itself is developed on the basis of permanent magnet DC brushless motor. With the development of electronic control technology, the waveform of the three-phase brushless motor power supply has evolved from square wave input to sine wave input and synchronous control, forming a synchronous operation three-phase brushless motor, also known as synchronous motor. Nowadays, motors with a single square wave (trapezoidal wave) power input that does not involve synchronous control technology are still referred to as three-phase brushless motors.
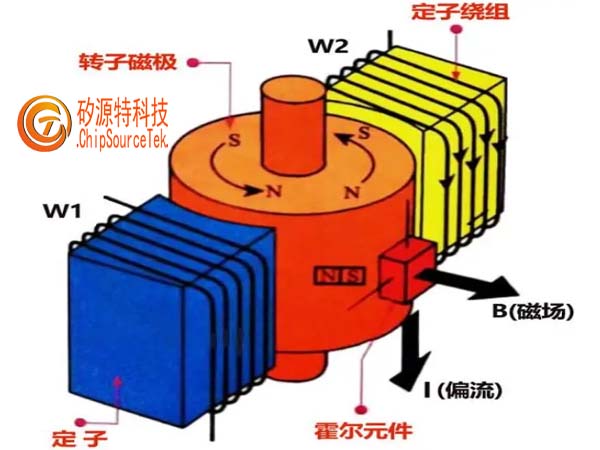
A three-phase brushless motor is more complex than a permanent magnet DC brushless motor because electronic commutation technology changes the structural form of the motor, holding the energized coil stationary and generating a rotating magnetic field that causes the magnetic steel to rotate, and the control signal changes accordingly with the rotation of the rotor.
A three-phase brushless motor is a typical mechatronics product composed of a motor, a sensor, and a driver. The position sensor detects the magnetic pole signal of the rotor, and the controller compares this signal for logical processing and generates corresponding switch signals. The switch signals trigger the power switch devices in the driver in a certain order, and distribute the power current to each phase winding of the motor in a certain logical relationship, Rotate the motor and generate continuous torque, so that the three-phase brushless motor can operate.
Principle of three-phase DC brushless motor
The working principle of brushless DC motor 1 is that due to the commutation of the brushes, the magnetic field generated by the * magnetic steel and the magnetic field generated by the armature winding after being energized remain perpendicular during the operation of the motor, resulting in a large torque and causing the motor to operate. The operating principle of a brushless DC motor is basically the same as that of a brushless DC motor, that is, under a magnetic field with a constant flux density distribution, the total amount of current flowing into the armature winding is constant to generate a constant torque, and the torque is only related to the magnitude of the armature current. The operation of a brushless DC motor also relies on the rotor position sensor to detect the position signal of the rotor. Through the commutation drive circuit, the power switch tubes connected to the armature winding are driven to turn on and off, thereby controlling the energization of the sub winding and generating a rotating magnetic field on the stator, dragging the rotor to rotate. As 636f7079e79fa5e9819331333433623738 rotates around the rotor, the position sensor continuously sends signals to change the energized state of the armature, so that the direction of current in the conductor under the same magnetic field remains unchanged. Therefore, a constant torque can be generated to operate the brushless DC motor. From the composition of a brushless DC motor, it is actually a closed-loop system composed of the motor body, electronic switch circuit, and rotor magnetic steel position sensor.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











