How to prevent reverse charging of lithium batteries
Time:2023-10-07
Views:632
Lithium batteries are commonly used in many device applications that require backup power, such as real-time clocks (RTCs) and storage devices. When a lithium battery is not a single power source in the circuit, there is a risk of fire or explosion if the battery is accidentally connected to a power source that can charge the battery. This application note provides the information required to connect a lithium battery in a backup power switch circuit to comply with UL standards. Specifically, UL standard 60950-1 describes guidelines for lithium batteries.
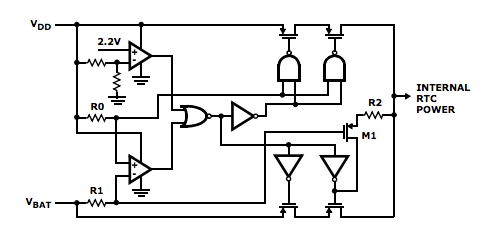
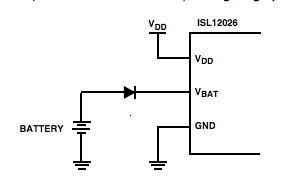
Intersil RTC protection circuit with battery switching function
All Intersil RTCs with battery switching function (such as the ISL12026 series) have internal protection circuits to prevent reverse charging. Figure 1 shows the internal switching circuit, illustrating complementary control that disables one power input while enabling another power input. Two series of MOSFET switches provide safety switches and redundancy. It is also the path from VDD to VBAT, through MOSFETs (M1) used to pull up the VBAT switch gate and two 200 Ω resistors (R1 and R2). If the M1 gate is short circuited, the current flowing through resistors R1 and R2 will limit the charging current of the lithium battery (up to 9.25mA when VDD=5.5V and VBAT=1.8V).

To meet the complete UL safety requirements, it is necessary to add a series Schottky diode to the VBAT input of these products. External diodes are used to provide protection in the event of internal MOSFET and series resistor failures. Figure 2 shows the actual circuit with an external protective diode. (Please note that high value series resistors will provide similar protection, but will limit the normal operating range.)

Only use silicon diodes or Schottky diodes with low reverse current. The typical reverse current recommended by UL is 1 μ A. Some diodes with low reverse current that can be used include but are not limited to BAS40, BAS70, and BAT54 diodes.
Where Q is the nominal capacity of the battery (mAh), and tp is the total allowed charging time (percentage). For button type batteries, the TP is 3%. For cylindrical batteries, the tp is 1%.
Example: A 1000mAh button battery can be used for five years.
According to formula 2, Ic is 30mAh (1000mAh x 3% (button type battery)=30mAh).
According to formula 1, a reverse current of 0.7 is required μ Diodes of A or smaller (30mAh ÷ service time (5 years x 365 days x 24 hours)=0.7 μ A) .
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











