Principle of implementing audio signal detection
Time:2023-08-11
Views:761
The frequency range that can be heard by the human ear is approximately 20 Hz to 20000 Hz. This range can include single tones, such as transformer buzzing or white noise from the radio system. This is not to say that these sounds are ideal in audio systems. High intensity such sounds can damage hearing. Human speech, music, and natural sounds have constantly changing frequencies. Therefore, an audio detector should record frequency changes and select useful audio signals based on these changes.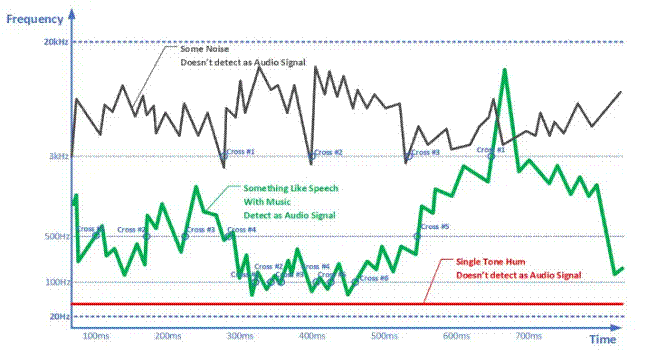
Figure 1 shows the working principle of audio signal detection. Dialogue Semiconductor

Figure 1 shows the working principle of audio signal detection. Dialogue Semiconductor
The basic principle of audio signal detection is shown in Figure 1. The system design considers three reference frequencies: 100 Hz, 500 Hz, and 3 kHz. For a given signal, the system calculates the number of times the frequency of the signal crosses the reference frequency within a certain period of time. Consider only the crossover from low frequency to high frequency; For example, 50 Hz to 150 Hz will be counted towards 100 Hz, while 150 Hz to 50 Hz will not be counted towards 100 Hz. If the signal intersects with either of the two reference frequencies a minimum of the number specified in Table 1, the design will consider the signal as audio.
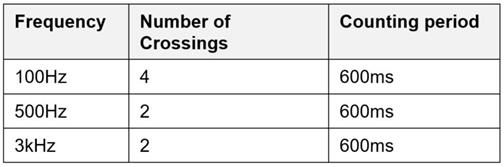
Table 1 Detects frequency crossover of audio signals; These numbers can be adjusted according to user needs through I 2C. Dialogue Semiconductor
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











