Discuss the understanding of current ripple and its impact on current driven devices
Time:2023-08-09
Views:774
Cognition of output ripple
Ripple current
Ripple current or voltage refers to the higher-order harmonic components in the current, which can cause changes in the amplitude of the current or voltage, possibly leading to breakdown. As an AC component, it can dissipate on the capacitor. If the ripple component of the current is too large, exceeding the maximum allowable ripple current of the capacitor, it can cause the capacitor to burn out;
Ripple current and ripple voltage
In some materials, these two are referred to as "ripple current" and "ripple voltage", meaning the ripple current/voltage value that a capacitor can withstand. They have a close relationship with ESR and can be expressed by the following formula:
Urms=Irms × R
In the formula, Urms represents the ripple voltage
Irms represents ripple current
R represents the ESR of the capacitor
When the ripple voltage increases, the ripple current also increases, which is why capacitors are required to have lower ESR values. After adding ripple current, the equivalent series resistance (ESR) inside the capacitor causes heat generation, which affects the service life of the capacitor. Generally, the ripple current is proportional to the frequency, so the ripple current is also relatively low at low frequencies.
Ripple definition and its relationship with lifespan:
Ripple current here refers to the RMS value of the AC current flowing through the capacitor, which manifests as pulsation or ripple voltage on the capacitor voltage. The maximum allowable ripple current of a capacitor is limited by environmental temperature, capacitor surface temperature (and heat dissipation area), loss angle (or ESR), and AC frequency parameters. Temperature is a decisive factor in the lifespan of electrolytic capacitor devices, so the heat loss generated by ripple will become a key reference factor for capacitor lifespan.
The influence of output ripple on LED
LED lighting has the characteristics of energy conservation, safety, and environmental protection. As an emerging technology field, it has undergone significant development in recent years. LED is a typical current driver device, which can accurately control the driving current and determine many parameters such as light efficiency, power efficiency, heat dissipation, etc. In order to reduce the current ripple coefficient, a trapezoidal integral PI control method is adopted in the high-frequency flyback switching power supply. By building a flyback switching power supply model based on MATLAB/Simulink, the trapezoidal integral PI control method was simulated. The simulation results show that the trapezoidal integral PI control method can effectively reduce the ripple current of the power supply, and the current ripple coefficient is reduced to 1.5%, achieving the control goal. Obviously, the output ripple can be easily controlled for LED lighting applications.
From the following two figures, it is evident that current ripple has almost no effect on the following factors: LED temperature, color temperature of output light, and frequency.
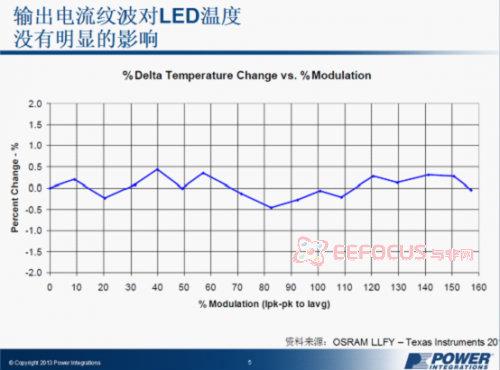
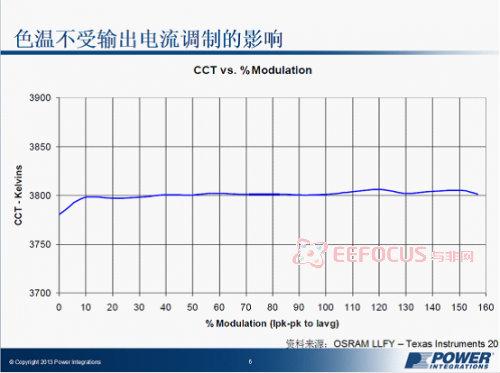





Figure 1: Effect of Output Current Ripple on LED Temperature

Figure 2: Effect of Output Current Modulation on Color Temperature
Netizens‘ viewpoint:
1.What is the acceptable level of current ripple for LED lighting applications?

2. What are the hazards of current ripple on LED lighting applications?

3. How to calculate the output ripple current? Is it better to choose a capacitor with a larger ripple current?

4. What are your tips for reducing output ripple? Everyone can share their usual design experiences~

|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











