The physical structure and application circuits of three main motors
Time:2023-06-09
Views:976
What types of motors are there?
Although the term ‘type of motor‘ is simple to say, with the development of technology, motors have become increasingly diverse, and therefore classification methods are also showing a trend of diversification. Classification can be based on the type of power supply, the principle of torque generation, motor structure, and application fields.
For example, when we classify according to the principle of torque generation and the structure of power supply, we will obtain the results shown in the following figure:
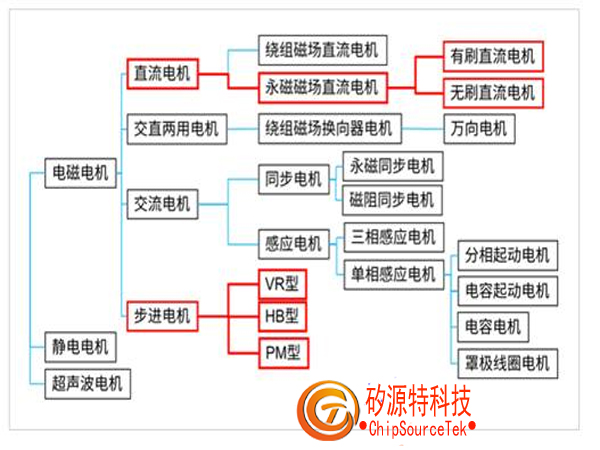
As shown in the above figure, there are many types of motors, but the ones that are convenient for electronic production are limited. In this article, we will introduce you to the three main types of motors suitable for electronic manufacturing and their applications.
What is a brushless DC motor?
The commonly used motor in electronic manufacturing is a "brush DC motor". Different motor manufacturers also have different names for this type of motor, such as "DC motor", "DC commutator motor", "brush motor", "DC commutator motor", and other names.
Brushed DC motor is a simple and easy to use motor. It does not need to prepare special electronic circuit to drive it. It can rotate as long as it is connected to Dry cell and other power supplies. Due to its ease of use and low price, it has become the most commonly used motor in electronic manufacturing.
It can also adjust rotation speed, set rotation direction, and control braking through PWM or a control IC called a "motor driver", and is therefore widely used in applications such as radio controllers and fans.
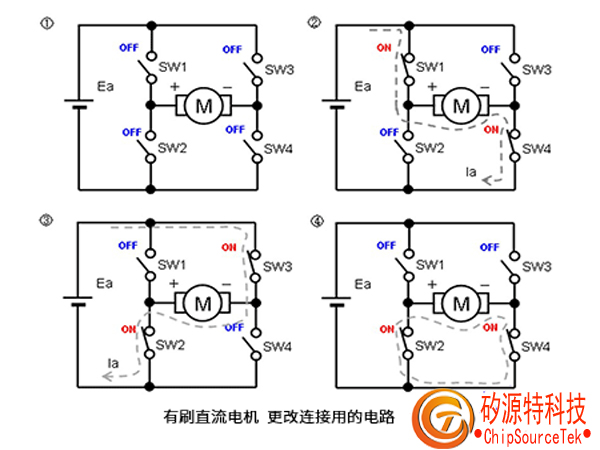
The figure shows a typical control method for a brushless DC motor - the "H-bridge circuit". The motor can be operated ① free/② forward/③ reverse/④ braking through the ON/OFF of four switches (actually transistors or FETs).
Although this type of motor has the advantages of ease of use, it also has some drawbacks. The interior of a brushless DC motor has a contact body called a "brush". If the brush is severely worn due to friction caused by rotation, the motor will be unusable. Turning for a few hours is not a problem, but if used continuously, the brushes will wear severely, requiring the entire motor to be replaced, and the motor cannot be reused.
In addition, sparks generated by the brush of the contact body are also one of the reasons for noise. In some cases, the odor generated by the operation of the brush DC motor is also a significant issue. Therefore, in some application scenarios, other options must be considered.
advantage
Power on to rotate
Low price
shortcoming
• Problems caused by brushes (lifespan, noise, odor, etc.)
What is a brushless DC motor?
The "brushless DC motor" solves the drawbacks caused by brushes by eliminating the brushes of the brushless DC motor. By removing the brushes, the internal contact bodies of the motor were eliminated, the number of components was reduced, and the performance of the motor in various aspects such as maintainability, weight, lifespan, motor efficiency, and high-speed rotation was ultimately improved. It can be said to be a groundbreaking motor. This type of motor does not operate on power and may be a bit troublesome to use, but it has high efficiency and long lifespan, making it often used in battery powered equipment.
The electronic circuit that rotates the motor will always monitor the rotation angle of the rotor connected to the output shaft (crankshaft) and switch the coil‘s power on at any time based on the angle. The role of the driving circuit is very important for the control of brushless DC motors. The driving circuit of brushless DC motors requires many electronic components, including position detection sensors, multiple power transistors and gate drivers, as well as microcontrollers to control them. Therefore, high requirements are placed on circuit design skills and software knowledge.
In recent years, there have been more and more brushless DC motors equipped with microcontroller controlled ICs or microcontrollers with brushless DC motor control functions. However, overall, the operation of brushless DC motors is still more complex than that of brushless DC motors.
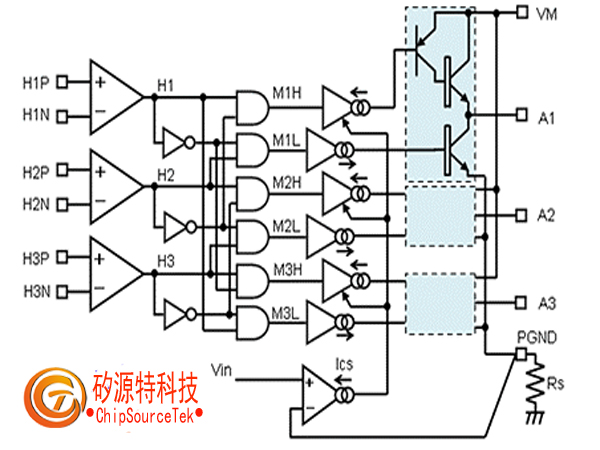
The driving circuit of a brushless DC motor. In addition to this circuit, a position detection sensor and a protection circuit for detecting overcurrent are also added, making the circuit large-scale.
By the way, the classification of brushless DC motors is quite complex. As the motor itself is driven by AC generated by the inverter, it can be considered as an "AC motor". However, it seems that brushless DC motors are often classified as "DC motors".
advantage
Light weight, long service life, and good motor efficiency
shortcoming
High price and complex driving circuit
What is a stepper motor?
A stepper motor is a motor that can control the rotation angle. The two types of motors introduced earlier are both used as power sources for long-term continuous rotation, while stepper motors are mainly used for position control.
The characteristic of a stepper motor is that every time a pulse signal is applied, the output shaft rotates at a fixed angle. The angle at which each pulse signal is input rotates is called the "step angle". For example, if it is a stepper motor with a step angle of 1.8 °, it will rotate once every 200 pulses. Therefore, it can be controlled according to methods such as "applying 100 pulses to rotate it for half a turn" or "applying 1000 pulses per second to rotate it for 5 revolutions per second", which can flexibly control its rotation speed, direction, and stop position.
Due to its ability to maintain torque even when the motor is stopped, stepper motors are also used in applications that require a fixed stop position.
Different from the way that the servo motor realizes the accurate stop position through the Servomechanism installed outside the motor, the stepping motor controls the position through its internal structure, so it has the characteristics of simple structure and high reliability. For applications such as CNC machine tools, 3D printers, and robotic arms that require high-precision position control, stepper motors have become indispensable components.
The driving circuit of a stepper motor that only needs to apply pulses to operate is relatively simple. However, if the load torque is too high or the speed is too fast, there will be problems such as out of step (mismatch between the number of pulses sent and the rotation angle) and noise. Therefore, in order to ensure stable operation, certain mechanical design skills are still needed.
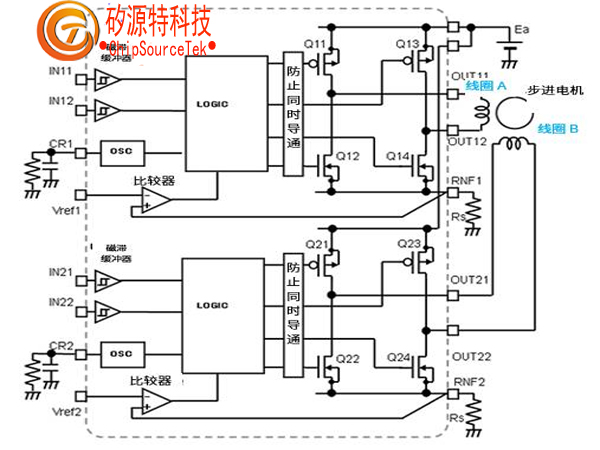
Driver IC used to drive stepper motors. At first glance, it may seem complex, but its principle is just an extension of the H-bridge circuit of a brushless DC motor. Additionally, it processes pulse signals, making it easy to control.
advantage
Easy position control
• With holding torque
High reliability
shortcoming
Step by step rotation, resulting in unsmooth movement
Not suitable for long-term continuous rotation and high-speed rotation
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











