Trapezoidal control of brushless dc motor
Time:2022-11-21
Views:1547
Trapezoidal control is one of the simplest control methods for brushless DC (BLDC) motor. It applies square wave current to align the motor phase with the trapezoidal back EMF waveform of BLDC motor to obtain the best torque. BLDC trapezoidal control is applicable to the design of motor control systems for white goods, refrigeration compressors, HVAC blowers, condensers, industrial drives, pumps, robots and other applications.

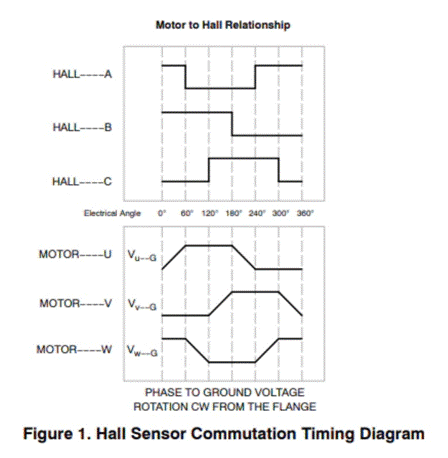

The MOSFET of the three-phase inverter that constitutes the drive motor has six on/off state combinations, thus generating six possible stator magnetic field directions in the rotating plane of the rotor magnetic field. Therefore, this method is also called six step method or 120 ° block commutation. According to the required rotation direction of the motor, the six possible inverter states must follow a specific sequence, so that the stator and rotor field directions can be arranged to generate maximum torque. Rotor position feedback is usually realized by Hall sensor (with sensor) installed on the motor or by sensing the back electromotive force of motor phase when rotating (without sensor), so as to determine the appropriate commutation timing.

Figure 1: Hall sensor reversing sequence diagram
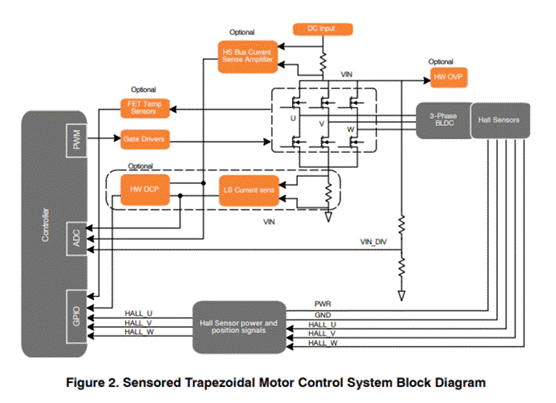
The ladder control with sensor can operate without any voltage or current feedback signal. It uses position feedback from the Hall sensor to determine the correct sequence of energizing each phase of the motor. The Hall sensor installed on the motor senses the rotor position through the Hall effect generated by the rotating magnetic field of the rotor permanent magnet. Even when starting, proper commutation can be carried out, because the rotor position information also exists even at zero speed.

Figure 2: Block Diagram of Sensorless Motor Ladder Control System
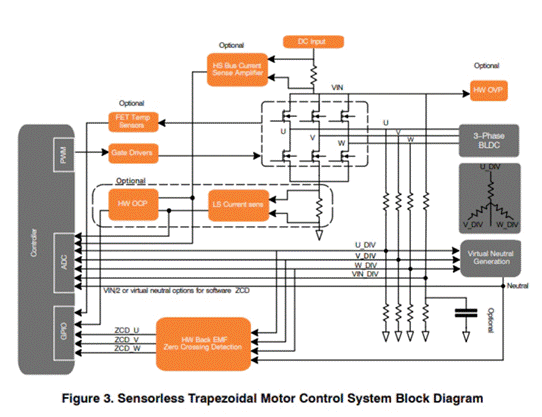
Sensorless trapezoidal control uses the back electromotive force generated by motor rotation to determine the proper motor commutation sequence. For ladder control, only two motor phases can be energized at a time. Since there is no current flow in the non energized phase, the back EMF can be directly sensed at this time. In the non energized phase, the back EMF increases or decreases linearly. Most of the back EMF position feedback techniques used in trapezoidal control rely on methods involving back EMF zero crossing detection (ZCD). The back EMF is monitored to determine when it crosses the reference point - half of the motor neutral voltage or DC bus voltage.

Figure 3: Sensorless motor ladder control system block diagram
Although trapezoidal control with sensors is easier to implement, because Hall sensors are installed in the motor, the cost is increased and more wiring is required from the motor, which is not feasible in some environments. Sensorless control is more complex, must be adjusted for specific loads or operating conditions, and may be difficult to start under heavy loads. However, sensorless control is ideal for applications where the load curve is known or where the load increases with speed, such as fans.
Other design considerations
When considering BLDC motor control design for your application, you also need to consider some key design factors, including:
◆ Overcurrent protection (hereinafter referred to as "OCP") - hardware, software or both can realize OCP to limit current and mitigate hard faults.
◆ Overvoltage protection (OVP) - hardware, software or both can protect the motor from damaging voltage.
◆ Over temperature protection (OTP) - It is very important to monitor the operating temperature of MOSFET in the inverter, especially in the environment with a wide temperature range.
◆ Selection of MOSFET - Onsemi‘s comprehensive high-efficient shielded gate channel MOSFET product portfolio can be customized according to your specific design requirements to achieve excellent performance of the motor control system.
The highly integrated motor control scheme can save energy. The advantages of trapezoidal BLDC control include simple control algorithm, high efficiency, simple motor, long service life and lower operating cost. The combination of trapezoidal control with basic protection and design technology to improve the control and accuracy of the motor is one of the most efficient methods to drive electric tools and robot motors.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











