Some points that every electronic engineer should know about oscilloscope
Time:2022-11-05
Views:1801
Among all the test equipment that electronic engineers and technicians need to use, oscilloscope is undoubtedly the most useful one. The powerful function of oscilloscope can help electronic engineers and technicians quickly and accurately capture the voltage (or current and other parameters) measurement values that change with time, while any other equipment in the laboratory can not easily complete such measurement.
 The key to becoming an oscilloscope expert is to first understand the basic knowledge of oscilloscopes, and then use this basic knowledge to expand learning. The following brief article will introduce some key points and common problems encountered by some new users in the basic use of oscilloscope. This will help us quickly understand the oscilloscope and find the correct learning direction. With the extension of learning time, we can make almost any measurement after using the oscilloscope for a certain time, and finally become more skilled and professional in the testing field.
The key to becoming an oscilloscope expert is to first understand the basic knowledge of oscilloscopes, and then use this basic knowledge to expand learning. The following brief article will introduce some key points and common problems encountered by some new users in the basic use of oscilloscope. This will help us quickly understand the oscilloscope and find the correct learning direction. With the extension of learning time, we can make almost any measurement after using the oscilloscope for a certain time, and finally become more skilled and professional in the testing field.

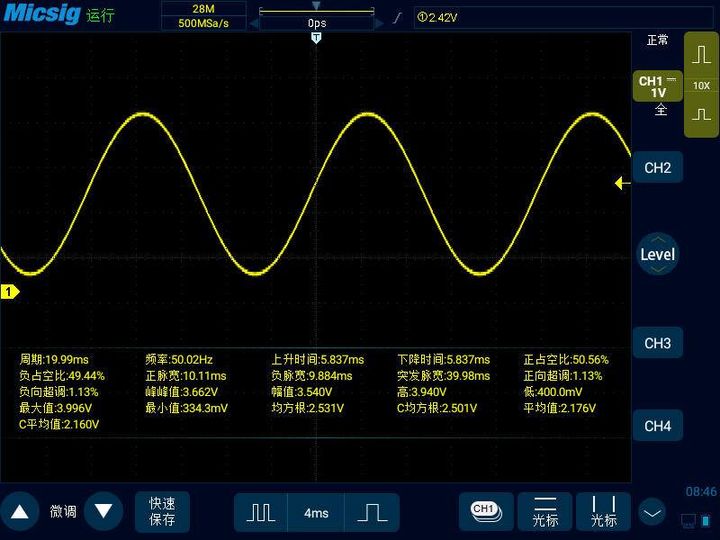
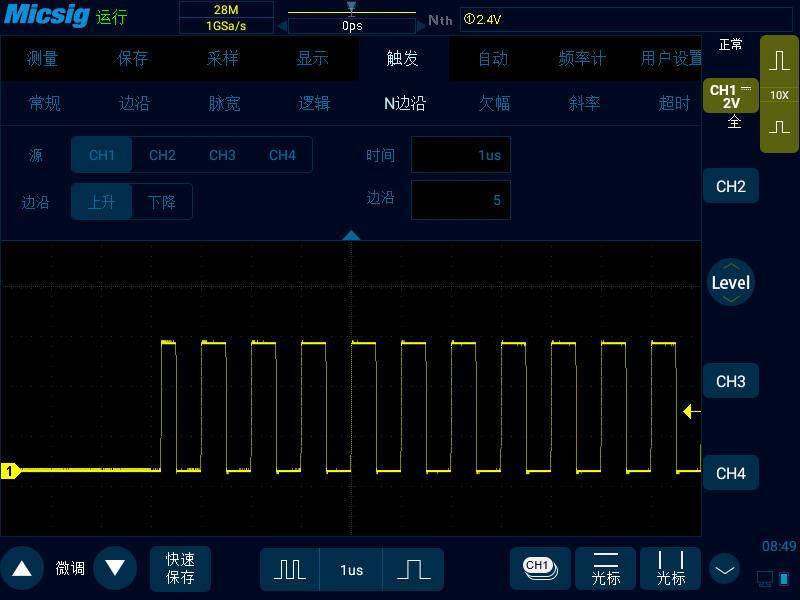
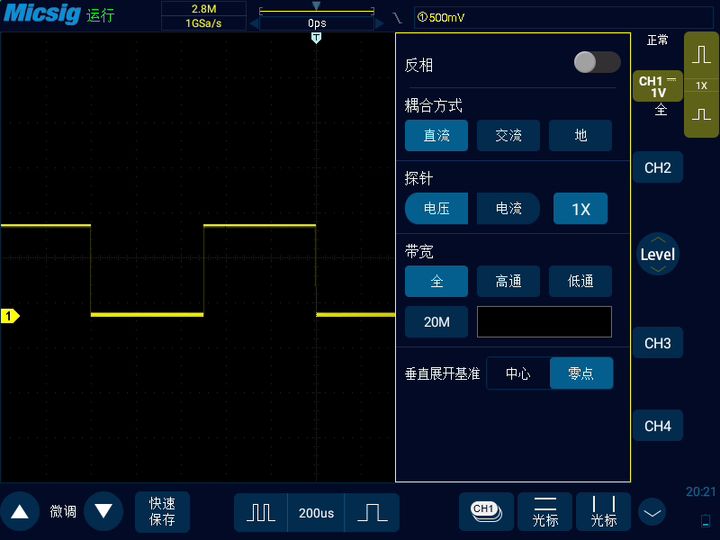
Oscilloscope is widely used in manufacturing, circuit design and other industries. It is a basic necessary tool for troubleshooting, signal integrity and simple understanding of the working principle of electronic circuits.
Although the whole buttons, knobs, probes, related probe accessories and color displays of modern oscilloscopes look very complex, which makes people who want to learn shrink back. But in fact, don‘t let the complex appearance of the oscilloscope scare you. As long as you master some basic skills, it is a very simple and easy to use device. Moreover, the current advanced oscilloscope also has a full touch function, which means that all the original and complex key knob operations can be replaced by touch screen operations. If you have experienced the early key phone and the current smart phone, you can quickly understand the advantages of touch screen.

For the sake of simplicity, this article will only introduce the smart oscilloscope with full touch and Android system, Maxon STO1104C, as an example. With the progress of the times, the old traditional analog oscilloscope has been obviously eliminated, so it will not be repeated.
Grounding and safety
Before understanding the basic knowledge of the oscilloscope, we should first understand the proper grounding and safety of the oscilloscope to avoid personal injury and damage to the oscilloscope or any accessories connected to the oscilloscope. Improper connection of the probe will form a current path and damage the probe. To avoid electric shock, the oscilloscope must be connected to the ground through the grounding wire. In short, the metal part of the probe connected to the oscilloscope is directly connected to the safety grounding through the power line of the oscilloscope.
You can try to change the connection yourself using an ohmmeter. This is a low impedance connection mode. When the circuit under test is also connected to the ground, a loop will be formed, and very low impedance will cause excessive current in the circuit. The current carrying capacity of the probe‘s grounding wire quickly exceeds its rated value, and the wire suddenly disconnects, you may hear a loud noise!
The best way to solve this problem is to disconnect the grounding loop by isolating the circuit under test or grounding the oscilloscope. If the safety grounding of the oscilloscope fails, the best choice is to ensure that the circuit under test is not connected to the ground safety grounding. Use an isolated oscilloscope or differential probe, or choose to use an isolated power supply or battery to power the test circuit. Be careful when using USB connector to supply power to the circuit under test, because such equipment is usually not isolated from the ground, and will still encounter the problem of ground loop.

What is an oscilloscope?
The oscilloscope can measure the voltage waveform of the measured signal through the voltage sensor (the most common oscilloscope voltage probe) or some other sensors (such as pressure sensor, current probe, noise meter, etc.). The graph generated by the oscilloscope measures the voltage on the vertical axis and represents the signal time on the horizontal axis. From the captured waveform, we can obtain data such as signal frequency, amplitude, period, phase, distortion, noise, DC, AC, duty cycle, rise/fall time, etc.

Basics
In addition to the display screen, there are three other important functions that constitute the oscilloscope. These functions are the trigger of the oscilloscope. Each grid in the vertical direction represents the volt value, and each grid in the horizontal direction represents the time value.
trigger
The trigger function is used for horizontal scanning of synchronous signals, which is essential for us to observe signals conveniently. By repeatedly displaying the trigger part of the input signal, the trigger makes the repeated waveform appear static on the display. The most basic and common trigger mode in oscilloscope is edge trigger. This is the trigger mode most likely to be used by most people when they first start using the oscilloscope. In addition, the oscilloscope has many other special and even complex trigger methods for responding to specific conditions, and can really make the oscilloscope a powerful measuring tool. These triggers include pulse width trigger, logic trigger, N edge trigger, under amplitude trigger, slope trigger, timeout trigger, video trigger, serial bus trigger, etc.

Vertical gear (volt/grid)
By adjusting the vertical gear of the oscilloscope, the shape of the waveform in the vertical direction can be enlarged and reduced. For example, if we set the vertical gear to 1V/grid and there are 10 grids in the vertical direction of the oscilloscope, the whole screen of the oscilloscope can display 10V waveform at most. It should be noted that this value is also related to the attenuation ratio of the probe. If we use a 10X probe, but we do not adjust the attenuation ratio of the oscilloscope channel (the default is 1X), then the correct reading will be 10 times different from the actual reading. Therefore, when using the oscilloscope, we should also pay attention to the attenuation ratio of the probe, and adjust the attenuation ratio of the channel to be consistent with the attenuation ratio of the probe.
Input coupling
Input coupling is another simple but commonly ignored or misunderstood function in oscilloscopes. It refers to the connection method used to connect electrical signals from one circuit to another, that is, from the circuit under test to the oscilloscope. You can set the input coupling mode as DC coupling, AC coupling or ground coupling. AC coupling only prevents the DC part of the signal from passing through, and you will see the waveform centered on zero level on the display. Ground coupling disconnects the input signal of the vertical control, allowing you to see the position of the zero level on the display. The DC coupling setting allows the display of all input signals, both DC and AC.

Horizontal gear (time/grid)
The horizontal gear function is also called time base, which can determine the time occupied by the waveform on the display screen. As with the above vertical gear control, the horizontal gear control can also scale the waveform, which controls the vertical direction of the waveform relative to the vertical gear and the horizontal direction of the waveform. If the time base is set to 10ms, each grid in the horizontal direction on the display screen represents 10ms, and the entire screen (assuming a total of 14 grids on the display screen) is equal to 140ms, representing that the entire waveform displayed is 140ms. By changing the size of the time base, you can easily observe the long or short time interval of the input signal.
performance
In terms of the attitude towards the speed of signals, most people generally only care about the frequency of signals, but do not care about the rise time of signals. In the standard sine wave, the rise time and frequency are simple mathematical relations. The typical formula used to determine whether the oscilloscope bandwidth is sufficient is 0.35 divided by the rise time. For example, it is necessary to measure the pulse with a rise time of 1ns, which means that the minimum bandwidth of the oscilloscope should be about 350MHz. But in practice, Fourier tells us that the actual waveform is the product of mixing fundamental wave and higher harmonic. Therefore, the higher the proportion of higher harmonics in the waveform, the shorter the rise time. Compared with the frequency of the signal, the rise time is more representative of the speed of the signal. So don‘t underestimate the low-frequency signal. As long as its rising edge bursts in an instant, it can cause a series of problems such as ringing, reflection and overshoot of the signal.
The sampling rate (Samples/second) and storage depth are also important considerations for oscilloscopes. The sampling rate indicates the ability of the oscilloscope to collect data points per second. The higher the sampling rate, the higher the authenticity and details of the waveform displayed by the oscilloscope, and the less likely the key information will be lost. If sine wave is to be measured, it is a general experience that the sampling rate of the oscilloscope should be at least 2.5 times of the highest frequency component of the signal to be measured. If square wave, pulse and other signal types are measured, the sampling rate shall be at least 10 times of the highest frequency component of the signal to be measured. The storage depth represents the maximum number of sampling points that can be saved on one screen of the oscilloscope. If the capacity of the oscilloscope to sample data is sufficient, but the capacity to store data is insufficient, then no matter how large the sampling rate is, it is useless. It‘s like we need to pour a glass of water. No matter how big the opening of the kettle is, or how fast the water is poured, if our cup is too small, it will never contain much water. Sampling rate=storage depth ÷ waveform recording duration, which is the relationship between the three. The duration of waveform recording is a parameter we control. The other two items are generally fixed parameters (oscilloscopes with large storage depth can also adjust the storage depth, but the upper limit is fixed).
probe
It is not too much to start a new article on the knowledge of oscilloscope probes. Most of us use the most passive probes with 1X or 10X attenuation ratio. When using the probe, pay attention to the maximum peak to peak voltage that the probe can withstand to prevent the capacitance load of the circuit under test from being too large. To measure high-speed signals, we often need active probes or differential probes.
cost performance
With the development and rise of domestic oscilloscope, oscilloscope is no longer a luxury for ordinary electronic enthusiasts, but a test instrument that most people can own. In the low-end field of oscilloscopes, the performance price ratio of the domestic oscilloscopes has completely challenged those imported oscilloscopes. Therefore, for most people, buying a domestic oscilloscope is a good choice!

Write at the end
Oscilloscope is the main instrument and equipment for product development and testing. They may seem complicated at first, but they are actually very easy to use. As long as you remember some basic knowledge and use her more, you will soon be considered as an oscilloscope expert of the company. With the increasing complexity and working frequency of electronic equipment systems, more and more application scenarios need to use oscilloscopes. Considering the long service life of oscilloscopes, it is very cost-effective to own and use an oscilloscope early.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |











