How to choose the right power chip
Time:2022-08-26
Views:1826
1、 Preface
What is a power chip? What does it do? What should be considered when selecting a power chip? The linear adjustment rate of input voltage and the relative influence of linear change of input voltage on output voltage? Here are some conceptual issues:
1. Output voltage load regulation rate: relative change of output voltage when load current changes
2. Output voltage accuracy: error range of device output voltage
3. Load transient response: when the load current changes rapidly from a small value to the maximum current, the output voltage fluctuates.
It depends on your application. For example, in the case of boosting, of course, only DC / DC can be used, because LDO is a voltage drop type and cannot be boosted.
In addition, take a look at their main characteristics:
DC / DC: high efficiency and high noise;
LDO: low noise and small static current;
Therefore, if it is used in the case of large voltage drop, DC / DC is selected because of its high efficiency, while LDO will lose most of its efficiency due to large voltage drop;
If the voltage drop is small, LDO is selected because of its low noise, clean power supply, simple peripheral circuit and low cost.
LDO is low dropout regulator, which means low dropout linear regulator, which is relative to traditional linear regulator. Traditional linear voltage regulators, such as 78xx series chips, require the input voltage to be more than 2V ~ 3V higher than the output voltage, otherwise it will not work normally. However, in some cases, such conditions are obviously too harsh, such as 5V to 3.3V, and the pressure difference between input and output is only 1.7V, which obviously does not meet the conditions. In view of this situation, LDO class power conversion chips are available.
LDO linear step-down chip: the principle is equivalent to a resistance voltage division to realize the step-down. The energy loss is large, and the reduced voltage is converted into heat. The larger the voltage difference and load current of the step-down, the more obvious the chip heating. This kind of chip has a large package and is convenient for heat dissipation.
LDO linear buck chips such as 2596, l78 series, etc.
DC / DC step-down chip: during the step-down process, the energy loss is relatively small and the chip heating is not obvious. The chip package is small and can realize PWM digital control.
DC / DC Buck chips such as tps5430 / 31, tps75003, max1599 / 61, tps61040 / 41
LDO is low dropout regulator, which means low dropout linear regulator, which is relative to traditional linear regulator. Traditional linear voltage regulators, such as 78xx series chips, require the input voltage to be more than 2V ~ 3V higher than the output voltage, otherwise it will not work normally.
However, in some cases, such conditions are obviously too harsh, such as 5V to 3.3V, and the pressure difference between input and output is only 1.7V, which obviously does not meet the conditions. In view of this situation, LDO class power conversion chips are available. There are many companies producing LDO chips, such as alpha, linear (LT), Micrel, national semiconductor, Ti, etc.
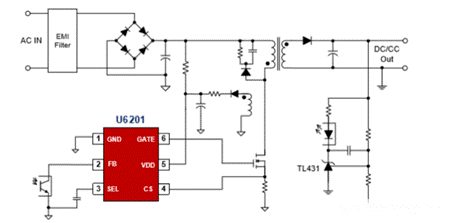
2、 What is an LDO (low pressure drop) regulator?
LDO is a linear regulator. A linear regulator uses transistors or FETs operating in its linear region to subtract excess voltage from the applied input voltage to produce a regulated output voltage. The so-called drop voltage refers to the minimum value of the difference between the input voltage and the output voltage required by the regulator to maintain the output voltage within 100 mV above or below its rated value.
 .
. LDO (low voltage drop) regulators with positive output voltages usually use power transistors (also known as transfer devices) as PNPs. This transistor allows saturation, so the regulator can have a very low voltage drop, usually about 200mV; In contrast, the voltage drop of a conventional linear regulator using NPN composite power transistors is about 2V. The negative output LDO uses NPN as its transfer device, and its operation mode is similar to the PNP device of the positive output LDO.
Newer developments use CMOS power transistors, which can provide the lowest voltage drop. With CMOS, the only voltage drop through the regulator is caused by the on resistance of the load current of the power supply device. If the load is small, the voltage drop generated in this way is only several tens of millivolts.
DC / DC means DC to DC (conversion of different DC power values). As long as this definition is met, it can be called DC / DC converter, including LDO. But generally speaking, the device that converts DC to DC by switching is called DC / DC.
LDO means low-voltage drop, which is explained by a paragraph: low-voltage drop (LDO) linear regulator has low cost, low noise and small static current, which are its outstanding advantages. It also requires few external components, usually only one or two bypass capacitors. The new LDO linear regulator can achieve the following indicators: output noise 30 μ 5. PSRR is 60dB, static current is 6 μ A. The voltage drop is only 100 mV.

The performance of LDO linear regulator can reach this level mainly because the regulator is a p-channel MOSFET, while the common linear regulator is a PNP transistor. The p-channel MOSFET is voltage driven and does not need current, so the current consumed by the device itself is greatly reduced; On the other hand, in the circuit using the PNP transistor, in order to prevent the PNP transistor from entering the saturation state and reducing the output capability, the voltage drop between the input and the output may not be too low; And the voltage drop on the p-channel MOSFET is approximately equal to the product of the output current and the on resistance. Since the on resistance of the MOSFET is very small, the voltage drop on it is very low.
If the input voltage and the output voltage are very close, it is best to choose LDO voltage regulator to achieve high efficiency. Therefore, LDO voltage regulator is mostly used in the application of converting the lithium-ion battery voltage to 3V output voltage. Although 10% of the battery‘s energy is not used in the end, the LDO regulator can still ensure that the battery‘s working time is long and the noise is low.
If the input voltage and the output voltage are not very close, it is necessary to consider switching type DCDC, because from the above principle, the input current of LDO is basically equal to the output current. If the voltage drop is too large, the energy consumed on LDO is too large and the efficiency is not high.
The DC-DC converter includes a step-up, a step-down. The DC-DC converter has the advantages of high efficiency, large output current and small static current. With the improvement of integration, many new DC-DC converters need only a few external inductors and filter capacitors. However, the output pulsation and switching noise of this kind of power controller are large and the cost is relatively high.
In recent years, with the development of semiconductor technology, the cost of surface mounted inductors, capacitors, and highly integrated power control chips has been continuously reduced and the volume has become smaller and smaller. Since MOSFETs with small on resistance can output large power, there is no need for external high-power FETs. For example, for an input voltage of 3V, an output of 5V / 2A can be obtained by using the nFET on the chip. Second, for small and medium power applications, a low-cost compact package can be used. In addition, if the switching frequency is increased to 1 MHz, it is also possible to reduce the cost and use inductors and capacitors with smaller sizes. Some new devices also add many new functions, such as soft start, current limiting, PFM or PWM mode selection.
In general, DCDC must be selected for boosting, and DC-DC or LDO should be selected for boosting. Cost, efficiency, noise and performance should be compared.
LDO has small volume and small interference. When the difference between input and output voltage is large, the conversion efficiency is low.
The advantages of DC-DC are high conversion efficiency and large current, but the output interference is large and the volume is relatively large.
LDO generally refers to linear voltage regulator - lowdropout, while DC / DC is the general term of linear and switching voltage regulators.
If your output current is not large (such as within 3a), and the input-output voltage difference is not large (such as 3.3V to 2.5V, etc.), you can use LDO voltage regulator (the advantage is that the ripple of the output voltage is very small). Otherwise, it is better to use a switch type regulator. If it is boosting, only a switch type regulator can be used (if the ripple control is not good, it will easily affect the system operation).
3、 Selection of LDO
When the designed circuit has the following requirements for shunt power supply:
1. High noise and ripple suppression;
2. Small PCB area, such as mobile phones and other handheld electronic products;
3. Inductors are not allowed for circuit power supply, such as mobile phones;
4. The power supply shall have the functions of instantaneous calibration and output state self inspection;
5. Low voltage drop of the regulator and low power consumption are required;
6. Low line cost and simple scheme are required;
At this time, LDO is the most appropriate choice to meet various requirements of product design. The above is the selection method of power supply chip. I hope it can help you. You need to choose according to different projects when designing.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is infringement or objection, please contact us to del |











