Audio equipment parameter analysis
Time:2022-06-29
Views:2054
For products of various industries, as equipment, there are various parameters. For the audio industry, speakers, sound sources and amplification equipment also have many parameter indicators. For most consumers, they do not understand the meaning of these parameters. The higher the better, the lower the better? And how much can these parameters really affect the final performance of the device sound?

Parameters cannot explain all audio device parameter analysis
With the digital transformation of audio equipment, manufacturers have also begun to pay more and more attention to the publicity of product parameters. One gorgeous "king of parameters" equipment has been born. Some of the sound performance is really good machines that can live up to these super parameters, and there are also many machines whose sound can hardly be heard. In the simulation era, most equipment never emphasized how powerful their parameters were. Even though the parameters of many classic products were not so good-looking, they were praised by countless consumers and enthusiasts.
These hard parameters are not omnipotent for audio products. It can only be said that the parameters of good-looking devices are often not ugly, but good-looking parameters do not necessarily mean that this product must be good to listen to. For consumers and enthusiasts, if they have not heard of products, they may also prefer products with excellent performance of some parameters, but what do these parameters mean, Are these parameters high enough to produce excellent sound? Let‘s take a look at the following articles!
Distortion and daring
Power amplifier, or power amplifier, is a very important part of sound system. Power amplifier is divided into electronic tube power amplifier and transistor power amplifier. The electronic tube power amplifier is a daring opportunity that many veteran enthusiasts like to talk about. Although compared with the ordinary transistor power amplifier, the venture has high cost, large volume and high power consumption, it has still won the support of the majority of music enthusiasts. Why?

Daring often has a lot of distortion, but there are still a lot of old burning pursuits
Due to the unique even harmonic distortion, the tube amplifier can easily restore the "loose, sweet and moist" timbre of a real musical instrument. It is also the even harmonic distortion. The test index of the electron tube power amplifier is generally lower than that of the transistor power amplifier. The total harmonic distortion of many classic famous machines even reaches more than 1%. For transistor amplifiers, it is easy to achieve a low distortion of 0.0%, but the sound of transistor amplifiers is somewhat too straightforward and stimulating compared with tube amplifiers. Therefore, after the gradual popularization of digital audio sources in the 1980s, the electronic tube power amplifier made a comeback in the fever audio market, making an indelible contribution to neutralizing the "cold, hard and dry" of digital audio sources.
Channel separation and sense of presence
Channel separation is an important index of audio products, which refers to the degree of mutual crosstalk between two channels. If the crosstalk is too large, the stereo sense will be weakened. In order to pursue excellent measurement, some audio products even make great efforts, and even pay the price of affecting other aspects of sound quality. Is it worth it to achieve a channel separation of 90 to 100 dB?

The separation degree of current mainstream equipment is no longer a problem
In fact, the live music will not only have two channels. Although people have two ears, the two ears are not completely isolated. People who have heard symphonic music at the scene know that in the middle seat of row 10-20, that is, the so-called emperor seat, the vocal tract separation of people‘s ears is more than 60 dB. This has been a controversial topic in the sound industry for many years. Is it meaningful to excessively pursue the channel separation index?
Jitter
Jitter was first discovered by Toshiba engineers in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Time jitter distortion is an abstract concept. For example, Mr. Xiao Ming has class at 7:30 every morning, but Mr. Xiao Ming may arrive in the classroom at 7:28 today and 7:33 the day after tomorrow. That is to say, the early or late time of class, which should have happened on time, is called the shaking of Mr. Xiao Ming‘s timeline. When jitter distortion is large, for example, teacher Xiao Ming comes half an hour late today and half an hour early tomorrow, students will complain. Similarly, the signal transmission of digital audio composed of 0 and 1 also has this problem.

DCS, the world‘s top sound source brand, also has its own suit clock
The standard I2S digital audio transmission has a dedicated time signal channel. Even so, jitter is still inevitable. So there are various independent clocks to reduce jitter distortion. With the rapid development of telecommunications technology, the clock is becoming smaller and more high-performance, so the impact of jitter distortion on sound quality is becoming less important. When using the same monitoring equipment, how much difference can users really hear between a 50 ppm clock and a 10 ppm clock? But jitter has become a selling point of fever equipment in the successful marketing of famous audio brands and an important indicator of the audio market. Some manufacturers even hype the temperature compensation crystal oscillator as a selling point of equipment, which is going
astray.
Signal to noise ratio and audible level
First of all, the definition of signal-to-noise ratio refers to the ratio of the normal sound signal played back by the speaker to the noise signal (power) without signal. Expressed in dB. For example, the signal-to-noise ratio of a speaker is 80dB, that is, the output signal power is 10^8 times the noise power, and the standard deviation of the output signal is 10^4 times the noise standard deviation. The higher the signal-to-noise ratio, the lower the noise.

SNR is important, but whether it can be distinguished is another problem
"Noise" is simply defined as "signals generated by the equipment during processing", which are independent of the input signal. For MP3 players, signal-to-noise ratio is an important parameter. It refers to the ratio between the maximum undistorted sound signal intensity produced by the sound source and the noise intensity emitted at the same time. It is called signal/noise ratio for short. It is usually expressed in s/n, and the unit is dB. For the player, the higher the value, the better. At present, the signal-to-noise ratio of MP3 players is 60dB, 65dB, 85dB, 90dB, 95dB, etc. when we choose MP3 players, we generally choose more than 60dB. However, even if this parameter meets the requirements, it does not necessarily mean that the machine is good. After all, it is only one of the parameters to be considered in MP3 performance parameters.
However, in terms of the audible level of human ear, the sensitivity to the signal-to-noise ratio is basically about 90dB. If the signal-to-noise ratio of the equipment is higher than 90dB, the audible change of human ear will be smaller. However, the performance in detail can be heard in terms of the auditory sense. However, if a signal-to-noise ratio is compared with 95dB and 105dB, the audible change may be almost zero. For MP3 player, the parameter of signal-to-noise ratio is determined by the decoding chip and the circuit. The decoding chip determines the highest possible signal-to-noise ratio, while the circuit ensures that the signal-to-noise ratio is reduced as little as possible. However, the signal-to-noise ratio of the chip is an average value, which means that the chip manufacturer cannot guarantee that each decoding chip is the same signal-to-noise ratio. If the nominal signal-to-noise ratio of a decoding chip is 100dB, that means the signal-to-noise ratio of this chip may be between 98-102db. That is to say, if the decoding chip used for an MP3 is 100dB, Then the audio output signal-to-noise ratio of this player cannot be higher than 102dB.
Flatness of frequency response curve
Many users believe that the frequency response curve of audio equipment must be straight, otherwise it must not be a good equipment. This thesis should be viewed separately. Generally speaking, the audio source products of audio equipment, that is, CD players and DAC decoders, generally have different lines in the high frequency band according to the different analog filters used. The sound source products using Butterworth filter often have a roll down of 1-3 dB at the high frequency of 15-20KHz. Products using Chebyshev and elliptic filters also have some fluctuating lines at high frequencies. Some low-end consumer audio source products, such as low-end MP3 players, simply use digital filtering to cut off the high frequencies above 20K without using analog filters. Although the frequency response curve looks flat, it actually contains a lot of high-frequency digital clutter, which makes the listening feel thin and cold. This is the so-called digital sound. However, for sound source equipment, the so-called "digital flavor" and "analog flavor" have no positive or negative meanings, but represent their own music style characteristics.
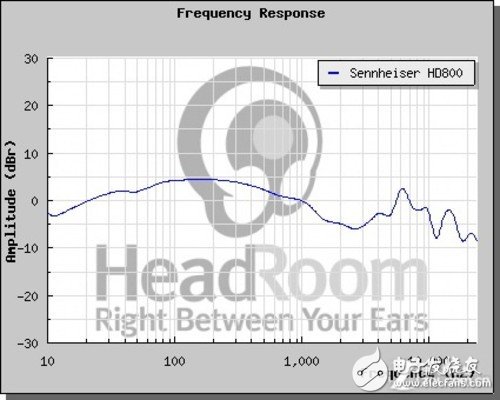
Frequency response curve can not explain everything
The frequency response curve of headphones is a very complex situation. First of all, almost all the frequency response curves of earphones are corrected, and the adjustment of frequency response curves of earphones is often based on comparison. It is difficult to explain the problem simply by discussing the frequency response curve of a certain earphone.
Summary:
Among the enthusiasts, there are always the parameter party, the technology party and the subjective listening party. In fact, the issue of who is right and who is wrong has been debated for countless years. After all, people on both sides disagree with each other. However, for parameters, they really can not 100% explain how a device is. At least, they should listen to them. Understanding parameters, having correct sound tendency and judgment ability are the most important.

Parameters cannot explain all audio device parameter analysis
With the digital transformation of audio equipment, manufacturers have also begun to pay more and more attention to the publicity of product parameters. One gorgeous "king of parameters" equipment has been born. Some of the sound performance is really good machines that can live up to these super parameters, and there are also many machines whose sound can hardly be heard. In the simulation era, most equipment never emphasized how powerful their parameters were. Even though the parameters of many classic products were not so good-looking, they were praised by countless consumers and enthusiasts.
These hard parameters are not omnipotent for audio products. It can only be said that the parameters of good-looking devices are often not ugly, but good-looking parameters do not necessarily mean that this product must be good to listen to. For consumers and enthusiasts, if they have not heard of products, they may also prefer products with excellent performance of some parameters, but what do these parameters mean, Are these parameters high enough to produce excellent sound? Let‘s take a look at the following articles!
Distortion and daring
Power amplifier, or power amplifier, is a very important part of sound system. Power amplifier is divided into electronic tube power amplifier and transistor power amplifier. The electronic tube power amplifier is a daring opportunity that many veteran enthusiasts like to talk about. Although compared with the ordinary transistor power amplifier, the venture has high cost, large volume and high power consumption, it has still won the support of the majority of music enthusiasts. Why?

Daring often has a lot of distortion, but there are still a lot of old burning pursuits
Due to the unique even harmonic distortion, the tube amplifier can easily restore the "loose, sweet and moist" timbre of a real musical instrument. It is also the even harmonic distortion. The test index of the electron tube power amplifier is generally lower than that of the transistor power amplifier. The total harmonic distortion of many classic famous machines even reaches more than 1%. For transistor amplifiers, it is easy to achieve a low distortion of 0.0%, but the sound of transistor amplifiers is somewhat too straightforward and stimulating compared with tube amplifiers. Therefore, after the gradual popularization of digital audio sources in the 1980s, the electronic tube power amplifier made a comeback in the fever audio market, making an indelible contribution to neutralizing the "cold, hard and dry" of digital audio sources.
Channel separation and sense of presence
Channel separation is an important index of audio products, which refers to the degree of mutual crosstalk between two channels. If the crosstalk is too large, the stereo sense will be weakened. In order to pursue excellent measurement, some audio products even make great efforts, and even pay the price of affecting other aspects of sound quality. Is it worth it to achieve a channel separation of 90 to 100 dB?

The separation degree of current mainstream equipment is no longer a problem
In fact, the live music will not only have two channels. Although people have two ears, the two ears are not completely isolated. People who have heard symphonic music at the scene know that in the middle seat of row 10-20, that is, the so-called emperor seat, the vocal tract separation of people‘s ears is more than 60 dB. This has been a controversial topic in the sound industry for many years. Is it meaningful to excessively pursue the channel separation index?
Jitter
Jitter was first discovered by Toshiba engineers in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Time jitter distortion is an abstract concept. For example, Mr. Xiao Ming has class at 7:30 every morning, but Mr. Xiao Ming may arrive in the classroom at 7:28 today and 7:33 the day after tomorrow. That is to say, the early or late time of class, which should have happened on time, is called the shaking of Mr. Xiao Ming‘s timeline. When jitter distortion is large, for example, teacher Xiao Ming comes half an hour late today and half an hour early tomorrow, students will complain. Similarly, the signal transmission of digital audio composed of 0 and 1 also has this problem.

DCS, the world‘s top sound source brand, also has its own suit clock
The standard I2S digital audio transmission has a dedicated time signal channel. Even so, jitter is still inevitable. So there are various independent clocks to reduce jitter distortion. With the rapid development of telecommunications technology, the clock is becoming smaller and more high-performance, so the impact of jitter distortion on sound quality is becoming less important. When using the same monitoring equipment, how much difference can users really hear between a 50 ppm clock and a 10 ppm clock? But jitter has become a selling point of fever equipment in the successful marketing of famous audio brands and an important indicator of the audio market. Some manufacturers even hype the temperature compensation crystal oscillator as a selling point of equipment, which is going
astray.
Signal to noise ratio and audible level
First of all, the definition of signal-to-noise ratio refers to the ratio of the normal sound signal played back by the speaker to the noise signal (power) without signal. Expressed in dB. For example, the signal-to-noise ratio of a speaker is 80dB, that is, the output signal power is 10^8 times the noise power, and the standard deviation of the output signal is 10^4 times the noise standard deviation. The higher the signal-to-noise ratio, the lower the noise.

SNR is important, but whether it can be distinguished is another problem
"Noise" is simply defined as "signals generated by the equipment during processing", which are independent of the input signal. For MP3 players, signal-to-noise ratio is an important parameter. It refers to the ratio between the maximum undistorted sound signal intensity produced by the sound source and the noise intensity emitted at the same time. It is called signal/noise ratio for short. It is usually expressed in s/n, and the unit is dB. For the player, the higher the value, the better. At present, the signal-to-noise ratio of MP3 players is 60dB, 65dB, 85dB, 90dB, 95dB, etc. when we choose MP3 players, we generally choose more than 60dB. However, even if this parameter meets the requirements, it does not necessarily mean that the machine is good. After all, it is only one of the parameters to be considered in MP3 performance parameters.
However, in terms of the audible level of human ear, the sensitivity to the signal-to-noise ratio is basically about 90dB. If the signal-to-noise ratio of the equipment is higher than 90dB, the audible change of human ear will be smaller. However, the performance in detail can be heard in terms of the auditory sense. However, if a signal-to-noise ratio is compared with 95dB and 105dB, the audible change may be almost zero. For MP3 player, the parameter of signal-to-noise ratio is determined by the decoding chip and the circuit. The decoding chip determines the highest possible signal-to-noise ratio, while the circuit ensures that the signal-to-noise ratio is reduced as little as possible. However, the signal-to-noise ratio of the chip is an average value, which means that the chip manufacturer cannot guarantee that each decoding chip is the same signal-to-noise ratio. If the nominal signal-to-noise ratio of a decoding chip is 100dB, that means the signal-to-noise ratio of this chip may be between 98-102db. That is to say, if the decoding chip used for an MP3 is 100dB, Then the audio output signal-to-noise ratio of this player cannot be higher than 102dB.
Flatness of frequency response curve
Many users believe that the frequency response curve of audio equipment must be straight, otherwise it must not be a good equipment. This thesis should be viewed separately. Generally speaking, the audio source products of audio equipment, that is, CD players and DAC decoders, generally have different lines in the high frequency band according to the different analog filters used. The sound source products using Butterworth filter often have a roll down of 1-3 dB at the high frequency of 15-20KHz. Products using Chebyshev and elliptic filters also have some fluctuating lines at high frequencies. Some low-end consumer audio source products, such as low-end MP3 players, simply use digital filtering to cut off the high frequencies above 20K without using analog filters. Although the frequency response curve looks flat, it actually contains a lot of high-frequency digital clutter, which makes the listening feel thin and cold. This is the so-called digital sound. However, for sound source equipment, the so-called "digital flavor" and "analog flavor" have no positive or negative meanings, but represent their own music style characteristics.

Frequency response curve can not explain everything
The frequency response curve of headphones is a very complex situation. First of all, almost all the frequency response curves of earphones are corrected, and the adjustment of frequency response curves of earphones is often based on comparison. It is difficult to explain the problem simply by discussing the frequency response curve of a certain earphone.
Summary:
Among the enthusiasts, there are always the parameter party, the technology party and the subjective listening party. In fact, the issue of who is right and who is wrong has been debated for countless years. After all, people on both sides disagree with each other. However, for parameters, they really can not 100% explain how a device is. At least, they should listen to them. Understanding parameters, having correct sound tendency and judgment ability are the most important.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is infringement or objection, please contact us to delete. thank you! |











