Crowbar circuit for overvoltage protection
Time:2022-05-05
Views:2200
The reliability of any electronic equipment depends on the design of hardware protection circuit. End users are likely to make all kinds of mistakes, so good hardware designers need to be responsible for the occurrence of hardware errors. Many protection circuits have their own common. The most common protection circuits are overvoltage protection circuit, reverse connection protection circuit, current surge protection circuit and noise protection circuit. In this paper, we discuss the crowbar circuit, which is a common overvoltage protection circuit in electronic equipment.
Required components
Working principle of crowbar circuit
The crowbar circuit will monitor the input voltage. When it exceeds the limit value, it will generate short-circuit current and blow the fuse. Once the fuse is blown, the power supply is disconnected from the load, so as to prevent the injury of high voltage. The circuit will produce a short circuit on the power line, just like a crowbar falling between the power lines, so it is called crowbar circuit.
The voltage at which the short circuit occurs depends on the zener voltage. The circuit is composed of a thyristor, which will be directly connected between the input voltage and ground, but the thyristor is off by default because the gate is grounded. When the input voltage exceeds the zener voltage, the zener diode is turned on, so the voltage is added to the thyristor gate, resulting in a short circuit between the input voltage and the ground. A short circuit will generate a huge current from the power supply, which will blow the fuse and disconnect the load from the power supply.
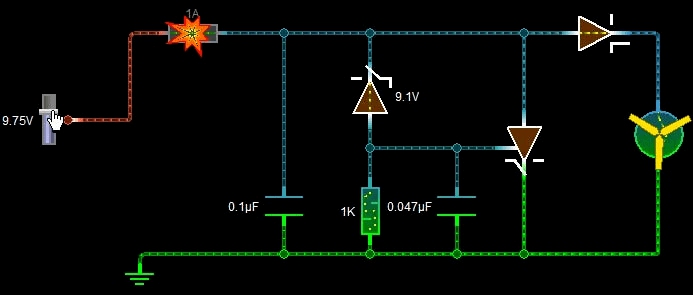
The above picture shows the process of overvoltage protection. When the voltage increases to 9.75v, the fuse blows. The functions of each component are as follows:
Required components
Fuse
Zener diode
Thyristor
Zener diode
Thyristor
Capacitance
Resistance
Schottky diode
Circuit schematic diagram of crowbar
The complete crowbar circuit is shown in the figure below.
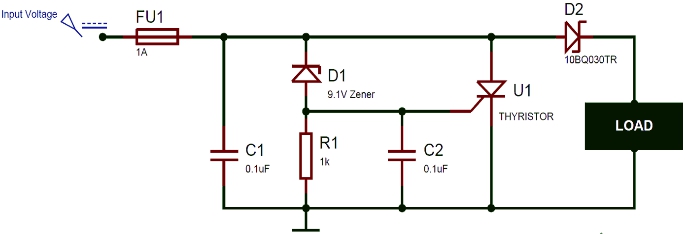
The blue probe part is the input voltage. The purpose of the circuit is to cut off the power supply when the power supply voltage exceeds 9.1v. The function of each part is discussed in the principle below.

The blue probe part is the input voltage. The purpose of the circuit is to cut off the power supply when the power supply voltage exceeds 9.1v. The function of each part is discussed in the principle below.
Working principle of crowbar circuit
The crowbar circuit will monitor the input voltage. When it exceeds the limit value, it will generate short-circuit current and blow the fuse. Once the fuse is blown, the power supply is disconnected from the load, so as to prevent the injury of high voltage. The circuit will produce a short circuit on the power line, just like a crowbar falling between the power lines, so it is called crowbar circuit.
The voltage at which the short circuit occurs depends on the zener voltage. The circuit is composed of a thyristor, which will be directly connected between the input voltage and ground, but the thyristor is off by default because the gate is grounded. When the input voltage exceeds the zener voltage, the zener diode is turned on, so the voltage is added to the thyristor gate, resulting in a short circuit between the input voltage and the ground. A short circuit will generate a huge current from the power supply, which will blow the fuse and disconnect the load from the power supply.

The above picture shows the process of overvoltage protection. When the voltage increases to 9.75v, the fuse blows. The functions of each component are as follows:
Fuse: the rated fusing current of the fuse shall be lower than the maximum rated current of the thyristor, but greater than the current consumed by the load. We should make sure that there is enough current to blow the fuse when the fault occurs.
0.uf capacitor: This is a filter capacitor; It will filter out spikes or other noises to prevent them from affecting the false triggering of the circuit.
9.1v zener diode: this diode determines the voltage value of overvoltage. We use 9.1v here. Designers can choose the parameters of the diode according to their own needs.
1K Ω resistance: This is a pull-down resistance to ensure that the gate of the thyristor is grounded and can be turned off before the zener diode is turned on.
47nF capacitor: each power switch such as thyristor needs a buffer circuit to suppress the voltage spike during switching and prevent the false triggering of thyristor. The capacitance value needs to be just able to filter out the noise, because high capacitance value will increase the delay of thyristor conduction after applying gate pulse.
Schottky diode: this diode is not necessary. It is only used for protection. It exists to ensure that we will not flow reverse current from the load end to damage the protection circuit. The reason for using Schottky diodes instead of ordinary diodes is that the voltage drop is small.
Limitation of crowbar circuit
Although crowbar circuit is widely used, it still has the following limitations:
1. The overvoltage value of the circuit completely depends on the zener voltage value, and there are few optional values of Zener diode.
Limitation of crowbar circuit
Although crowbar circuit is widely used, it still has the following limitations:
1. The overvoltage value of the circuit completely depends on the zener voltage value, and there are few optional values of Zener diode.
2. The circuit will also be affected by noise problems; Noise can cause false triggering and fuse blowing.
3. After the fuse is blown, the load can be operated again only after the voltage is normal.
4. The replacement of mechanical fuse requires energy, time and cost.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is infringement or objection, please contact us to delete. thank you! |











