How do MCU with different level signals communicate with each other?
Time:2022-04-13
Views:2231
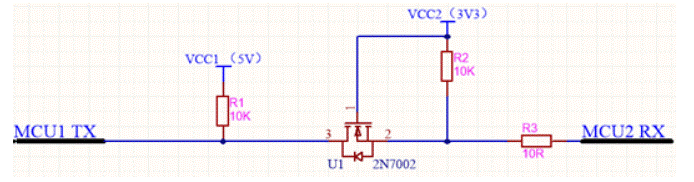
First, let‘s talk about the purpose of this circuit: when two MCU work under different working voltages (such as MCU 1 Working Voltage 5V; MCU 2 working voltage 3.3V), how to carry out serial communication between MCU 1 and MCU 2? Obviously, the corresponding TX and Rx pins cannot be directly connected, otherwise the MCU with low working voltage may be burned!
The "level bidirectional conversion circuit" in Figure 1 can realize serial communication between MCU with different VDD (chip working voltage).
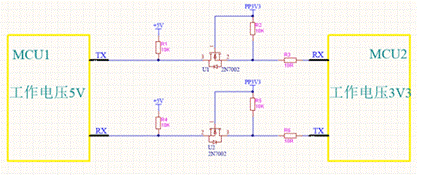
The core of the circuit is the MOS FET (2n7002) in the circuit. Its function is very similar to that of triode. It can be used as a switch to control the on and off of the circuit. However, compared with triode, MOS transistor has many advantages, which will be discussed in detail later.
Figure 2 is the physical 3D diagram and circuit diagram of MOS tube. In short, to use it as a switch, as long as VGS (on voltage) reaches a certain value, pins D and s will be on, and VGS will be cut off if it does not reach this value.
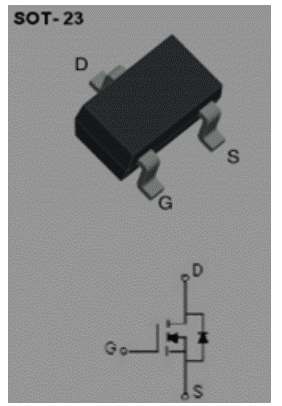
Function of MOS tube
How to apply 2n7002 to the above circuit and what role does it play? Now let‘s analyze it.
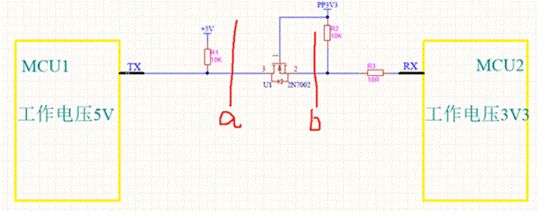
Figure 3
1. Analyze data transmission direction MCU 1 → MCU 2:
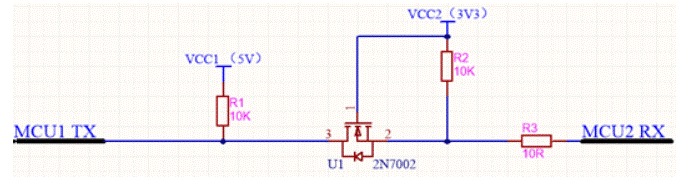
1) MCU1 TX sends high level (5V), and MCU2 Rx is configured as serial port receiving pin. At this time, s and D pins of 2n7002 (corresponding to pins 2 and 3 in Figure 4) are cut off, and diode 3 → 2 in 2n7002 is not in the direction. Then MCU2 Rx is pulled up to 3.3V by VCC2.
2) MCU1 TX sends low level (0V). At this time, s and D pins of 2n7002 are still cut off, but diodes 2 → 3 in 2n7002 are connected, that is, diodes in VCC2, R2 and 2n7002 and MCU1 TX form a loop. Pin 2 of 2n7002 is pulled low, and MCU2 Rx is 0V at this time. The circuit transfers data from MCU 1 to MCU 2 and achieves the effect of level conversion.
2. Analyze data transmission direction MCU 2 → MCU 1:
1) MCU2 TX sends high level (3.3V). At this time, the voltage difference of VGS (voltage difference between pins 1 and 2 in Figure 5) is about 0, 2n7002 is cut off, and diode 3 → 2 in 2n7002 is not connected. At this time, MCU1 RX pin is pulled up to 5V by VCC1.
2) MCU2 TX sends low level (0V). At this time, the voltage difference of VGS (voltage difference between pins 1 and 2 in Figure 5) is about 3.3V, 2n7002 is on, diode 3 → 2 in 2n7002 is not connected, and diode in VCC1, R1 and 2n7002 and MCU2 TX form a loop. Pin 3 of 2n7002 is pulled low, and MCU1 Rx is 0V at this time.
The circuit transfers data from MCU 2 to MCU 1 and achieves the effect of level conversion.
At this point, the circuit is analyzed. This is a bidirectional serial port level conversion circuit.
Advantages of MOS transistor
1. The source s, gate g and drain D of the FET correspond to the emitter e, base B and collector C of the triode respectively, and their functions are similar. Figure 5 (a) shows the pins of n-channel MOS transistor and NPN crystal triode, and figure 5 (b) shows the corresponding pins of p-channel MOS transistor and PNP crystal triode.
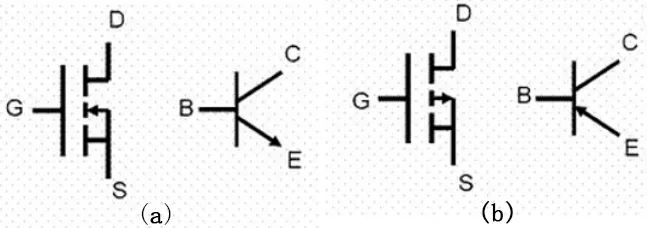
Figure 6
2. Field effect transistor is a voltage controlled current device, and the ID is controlled by VGS. Ordinary crystal triode is a current controlled current device, and the IC is controlled by IB. MOS pipe amplification factor is (transconductance GM) how many amperes can cause the drain current to change when the gate voltage changes by one volt. The crystal triode is the current amplification factor (beta) β) How much can the collector current change when the base current changes by one milliampere.
3. FET grid and other electrodes are insulated and do not generate current; When the triode works, the base current IB determines the collector current IC. Therefore, the input resistance of FET is much higher than that of triode.
4. Only most carriers participate in the conduction of FET; Triode has two kinds of carriers: majority carrier and minority carrier. Because the concentration of minority carrier is greatly affected by temperature, radiation and other factors, the temperature stability of FET is better than that of triode.
5. When the source of FET is not connected with the substrate, the source and drain can be used interchangeably with little change in characteristics. When the collector and emitter of triode are used interchangeably, their characteristics are very different, and the value of B will be greatly reduced.
6. The noise figure of FET is very small. FET should be selected in the input stage of low-noise amplification circuit and the circuit requiring high signal-to-noise ratio.
7. Field effect transistor and ordinary crystal triode can form various amplification circuits and switching circuits, but the manufacturing process of field effect transistor is simple, and it has excellent characteristics that ordinary crystal triode can not compare. It is gradually replacing ordinary crystal triode in various circuits and applications. At present, field effect transistor has been widely used in large-scale and very large-scale integrated circuits.
8. High input impedance and low driving power: due to the silicon dioxide (SiO2) insulation layer between the gate and source, the DC resistance between the gate and source is basically SiO2 insulation resistance, generally up to about 100m Ω, and the AC input impedance is basically the capacitive reactance of the input capacitor. Due to the high input impedance, there will be no voltage drop on the excitation signal, and it can be driven with voltage, so the driving power is very small (high sensitivity). General crystal triode must have base voltage VB and then generate base current IB to drive the generation of collector current. The driving of crystal triode requires power (VB × Ib)。
9. Fast switching speed: the switching speed of MOSFET has a great relationship with the capacitive characteristics of the input. Due to the existence of the capacitive characteristics of the input, the switching speed slows down. However, when used as a switch, it can reduce the internal resistance of the driving circuit and speed up the switching speed (the input is driven by the "perfusion circuit" described later to speed up the capacitive charge and discharge time). MOSFET only relies on multi carrier conduction and there is no minority carrier storage effect. Therefore, the shutdown process is very fast. The switching time is between 10-100ns and the working frequency can reach more than 100kHz. Due to the storage effect of a few carriers, the switch of ordinary crystal triode always lags behind, Affect the improvement of switching speed (at present, the switching power supply using MOS transistor can easily achieve the working frequency of 100k / S ~ 150k / s, which is unimaginable for ordinary high-power crystal triode).
10. No secondary breakdown: because the common power crystal triode has the phenomenon that when the temperature rises, it will lead to the rise of collector current (positive temperature current characteristic), and the rise of collector current will lead to the further rise of temperature and temperature, which will further lead to the vicious cycle of the rise of collector current. The withstand voltage Vceo of the crystal triode decreases gradually with the increase of the tube temperature, which leads to the continuous rise of the tube temperature and the continuous decline of the withstand voltage, which eventually leads to the breakdown of the crystal triode. This is a destructive thermoelectric breakdown phenomenon that leads to the damage rate of the TV switching power supply tube and line output tube accounting for 95%, also known as the secondary breakdown phenomenon.
MOS transistor has the opposite temperature current characteristics to ordinary crystal triode, that is, when the tube temperature (or ambient temperature) increases, the channel current decreases instead. For example; For a MOS FET switch with IDS = 10a, when the VGS control voltage remains unchanged, IDS = 3A at 250C. When the chip temperature rises to 1000C, IDS decreases to 2A. This negative temperature current characteristic that the channel current IDS decreases due to the temperature rise will not produce a vicious cycle and thermal breakdown.
That is, there is no secondary breakdown of MOS tube. It can be seen that the damage rate of MOS tube is greatly reduced by using MOS tube as switch tube. It is also an excellent proof that the damage rate of MOS tube is greatly reduced after using MOS tube to replace the past ordinary crystal triode in TV switching power supply in recent two years.
11. After the MOS transistor is turned on, its conduction characteristics are pure resistance: when the ordinary crystal triode is saturated, it is almost straight through, and there is an extremely low voltage drop, which is called saturation voltage drop. Since there is a voltage drop, that is; Ordinary crystal triode is equivalent to a resistance with very small resistance after saturation conduction, but this equivalent resistance is a nonlinear resistance (the voltage on the resistance and the current flowing through cannot comply with Ohm‘s law), while MOS transistor is used as a switch, there is also a resistance with very small resistance after saturation conduction.
However, this resistance is equivalent to a linear resistance. The resistance value of the resistance, the voltage drop at both ends and the current flowing comply with Ohm‘s law. When the current is large, the voltage drop is large, and when the current is small, the voltage drop is small. Since it is equivalent to a linear element after conduction, the linear element can be used in parallel. When such two resistors are connected in parallel, it has the function of automatic current balance. Therefore, when the power of one MOS tube is insufficient, it can be applied in parallel with multiple tubes without additional balancing measures (nonlinear devices cannot be applied in parallel directly).
The "level bidirectional conversion circuit" in Figure 1 can realize serial communication between MCU with different VDD (chip working voltage).

The core of the circuit is the MOS FET (2n7002) in the circuit. Its function is very similar to that of triode. It can be used as a switch to control the on and off of the circuit. However, compared with triode, MOS transistor has many advantages, which will be discussed in detail later.
Figure 2 is the physical 3D diagram and circuit diagram of MOS tube. In short, to use it as a switch, as long as VGS (on voltage) reaches a certain value, pins D and s will be on, and VGS will be cut off if it does not reach this value.

Function of MOS tube
How to apply 2n7002 to the above circuit and what role does it play? Now let‘s analyze it.

Figure 3
Look at Figure 3. If you follow lines a and B, cut off the circuit. Then the TX pin of MCU 1 is pulled up to 5V, and the RX pin of MCU 2 is also pulled up to 3.3V. The cut-off of pins s and D of 2n7002 (corresponding to pins 2 and 3 in Figure 3) is equivalent to two lines a and B, cutting off the circuit. In other words, this circuit can deliver the corresponding working voltage to the two MCU pins when 2n7002 is cut off.
1. Analyze data transmission direction MCU 1 → MCU 2:

1) MCU1 TX sends high level (5V), and MCU2 Rx is configured as serial port receiving pin. At this time, s and D pins of 2n7002 (corresponding to pins 2 and 3 in Figure 4) are cut off, and diode 3 → 2 in 2n7002 is not in the direction. Then MCU2 Rx is pulled up to 3.3V by VCC2.
2) MCU1 TX sends low level (0V). At this time, s and D pins of 2n7002 are still cut off, but diodes 2 → 3 in 2n7002 are connected, that is, diodes in VCC2, R2 and 2n7002 and MCU1 TX form a loop. Pin 2 of 2n7002 is pulled low, and MCU2 Rx is 0V at this time. The circuit transfers data from MCU 1 to MCU 2 and achieves the effect of level conversion.
2. Analyze data transmission direction MCU 2 → MCU 1:

1) MCU2 TX sends high level (3.3V). At this time, the voltage difference of VGS (voltage difference between pins 1 and 2 in Figure 5) is about 0, 2n7002 is cut off, and diode 3 → 2 in 2n7002 is not connected. At this time, MCU1 RX pin is pulled up to 5V by VCC1.
2) MCU2 TX sends low level (0V). At this time, the voltage difference of VGS (voltage difference between pins 1 and 2 in Figure 5) is about 3.3V, 2n7002 is on, diode 3 → 2 in 2n7002 is not connected, and diode in VCC1, R1 and 2n7002 and MCU2 TX form a loop. Pin 3 of 2n7002 is pulled low, and MCU1 Rx is 0V at this time.
The circuit transfers data from MCU 2 to MCU 1 and achieves the effect of level conversion.
At this point, the circuit is analyzed. This is a bidirectional serial port level conversion circuit.
Advantages of MOS transistor
1. The source s, gate g and drain D of the FET correspond to the emitter e, base B and collector C of the triode respectively, and their functions are similar. Figure 5 (a) shows the pins of n-channel MOS transistor and NPN crystal triode, and figure 5 (b) shows the corresponding pins of p-channel MOS transistor and PNP crystal triode.

Figure 6
2. Field effect transistor is a voltage controlled current device, and the ID is controlled by VGS. Ordinary crystal triode is a current controlled current device, and the IC is controlled by IB. MOS pipe amplification factor is (transconductance GM) how many amperes can cause the drain current to change when the gate voltage changes by one volt. The crystal triode is the current amplification factor (beta) β) How much can the collector current change when the base current changes by one milliampere.
4. Only most carriers participate in the conduction of FET; Triode has two kinds of carriers: majority carrier and minority carrier. Because the concentration of minority carrier is greatly affected by temperature, radiation and other factors, the temperature stability of FET is better than that of triode.
5. When the source of FET is not connected with the substrate, the source and drain can be used interchangeably with little change in characteristics. When the collector and emitter of triode are used interchangeably, their characteristics are very different, and the value of B will be greatly reduced.
6. The noise figure of FET is very small. FET should be selected in the input stage of low-noise amplification circuit and the circuit requiring high signal-to-noise ratio.
7. Field effect transistor and ordinary crystal triode can form various amplification circuits and switching circuits, but the manufacturing process of field effect transistor is simple, and it has excellent characteristics that ordinary crystal triode can not compare. It is gradually replacing ordinary crystal triode in various circuits and applications. At present, field effect transistor has been widely used in large-scale and very large-scale integrated circuits.
8. High input impedance and low driving power: due to the silicon dioxide (SiO2) insulation layer between the gate and source, the DC resistance between the gate and source is basically SiO2 insulation resistance, generally up to about 100m Ω, and the AC input impedance is basically the capacitive reactance of the input capacitor. Due to the high input impedance, there will be no voltage drop on the excitation signal, and it can be driven with voltage, so the driving power is very small (high sensitivity). General crystal triode must have base voltage VB and then generate base current IB to drive the generation of collector current. The driving of crystal triode requires power (VB × Ib)。
9. Fast switching speed: the switching speed of MOSFET has a great relationship with the capacitive characteristics of the input. Due to the existence of the capacitive characteristics of the input, the switching speed slows down. However, when used as a switch, it can reduce the internal resistance of the driving circuit and speed up the switching speed (the input is driven by the "perfusion circuit" described later to speed up the capacitive charge and discharge time). MOSFET only relies on multi carrier conduction and there is no minority carrier storage effect. Therefore, the shutdown process is very fast. The switching time is between 10-100ns and the working frequency can reach more than 100kHz. Due to the storage effect of a few carriers, the switch of ordinary crystal triode always lags behind, Affect the improvement of switching speed (at present, the switching power supply using MOS transistor can easily achieve the working frequency of 100k / S ~ 150k / s, which is unimaginable for ordinary high-power crystal triode).
10. No secondary breakdown: because the common power crystal triode has the phenomenon that when the temperature rises, it will lead to the rise of collector current (positive temperature current characteristic), and the rise of collector current will lead to the further rise of temperature and temperature, which will further lead to the vicious cycle of the rise of collector current. The withstand voltage Vceo of the crystal triode decreases gradually with the increase of the tube temperature, which leads to the continuous rise of the tube temperature and the continuous decline of the withstand voltage, which eventually leads to the breakdown of the crystal triode. This is a destructive thermoelectric breakdown phenomenon that leads to the damage rate of the TV switching power supply tube and line output tube accounting for 95%, also known as the secondary breakdown phenomenon.
MOS transistor has the opposite temperature current characteristics to ordinary crystal triode, that is, when the tube temperature (or ambient temperature) increases, the channel current decreases instead. For example; For a MOS FET switch with IDS = 10a, when the VGS control voltage remains unchanged, IDS = 3A at 250C. When the chip temperature rises to 1000C, IDS decreases to 2A. This negative temperature current characteristic that the channel current IDS decreases due to the temperature rise will not produce a vicious cycle and thermal breakdown.
That is, there is no secondary breakdown of MOS tube. It can be seen that the damage rate of MOS tube is greatly reduced by using MOS tube as switch tube. It is also an excellent proof that the damage rate of MOS tube is greatly reduced after using MOS tube to replace the past ordinary crystal triode in TV switching power supply in recent two years.
11. After the MOS transistor is turned on, its conduction characteristics are pure resistance: when the ordinary crystal triode is saturated, it is almost straight through, and there is an extremely low voltage drop, which is called saturation voltage drop. Since there is a voltage drop, that is; Ordinary crystal triode is equivalent to a resistance with very small resistance after saturation conduction, but this equivalent resistance is a nonlinear resistance (the voltage on the resistance and the current flowing through cannot comply with Ohm‘s law), while MOS transistor is used as a switch, there is also a resistance with very small resistance after saturation conduction.
However, this resistance is equivalent to a linear resistance. The resistance value of the resistance, the voltage drop at both ends and the current flowing comply with Ohm‘s law. When the current is large, the voltage drop is large, and when the current is small, the voltage drop is small. Since it is equivalent to a linear element after conduction, the linear element can be used in parallel. When such two resistors are connected in parallel, it has the function of automatic current balance. Therefore, when the power of one MOS tube is insufficient, it can be applied in parallel with multiple tubes without additional balancing measures (nonlinear devices cannot be applied in parallel directly).
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is infringement or objection, please contact us to delete. thank you! |











