Eight circuit fault detection methods
Time:2022-03-01
Views:2282
Electronic circuit troubleshooting can generally be detected by input to input sequence or by reverse method from output to input. No matter from which direction, electronic circuit fault detection can generally be judged by the following eight methods.
Method 1: direct observation
In case of circuit failure, usually the instrument will not be used for measurement immediately, but the visual observation is used to find the possible abnormal parts of the circuit. The direct observation method is divided into no power and power on detection.
Power failure detection is to check whether the level and polarity of the power supply voltage meet the circuit requirements; Whether the polarity of electrolytic capacitor, the pin position of diode and triode and the pin position of integrated circuit have problems such as false soldering, wrong soldering and crossing; Whether the wiring is unreasonable; Whether the circuit of the printed board is broken during printing; Whether the resistance and capacitance are obviously burnt.
The power on inspection is mainly to observe whether the components have overheating, smoke and obvious burning smell, and whether the filament of electronic tube and oscilloscope tube has high-voltage ignition and other problems.
Method 2: test with Multimeter
Multimeter detection is mainly to check the static working point, in which the resistance value and DC working state in the power supply system, triode, integrated block and circuit of electronic circuit can be detected by multimeter. Check to see if the value is normal.
Method 3: signal tracing method
In a complex circuit, you can access a signal at the input end, and then observe the waveform and amplitude changes one by one from the front stage to the rear stage or from the rear stage to the front stage through the oscilloscope, and finally check which one is abnormal.
Method 4: comparison method
The comparison method is more intuitive. It mainly compares the parameters of the suspected fault circuit with the same circuit in normal working state, finds out whether there is a value with large parameter difference, then analyzes the fault cause, and finally judges the fault location.
Method 5: substitution method
For the electronic circuit with no obvious fault, when the fault point cannot be judged visually, the existing same components can be used for replacement, and the fault judgment time can be shortened by observing whether the circuit changes.
Method 6: bypass inspection
If there is parasitic oscillation in the circuit, the capacitor with a certain capacity can be used to bridge the capacitor between the place to be checked or the reference grounding point, and then observe whether the oscillation exists. If the oscillation disappears, it indicates that the oscillation is generated in the front stage circuit or nearby circuit. If not, move back and continue to look for checkpoints. When selecting capacitors, it should be noted that the bypass capacitance should not be too large and can better eliminate adverse signals.
Method 7: short circuit inspection
The short circuit inspection method is that we actively create a temporary short circuit to short circuit some circuits. The amplification circuit shown in the figure below, in which the collector voltage of T2 measured by multimeter is 0. Then we suspect that there is an open circuit in L1 circuit, and then create a temporary short circuit at both ends of L1. At this time, if the value of vc2 is normal, it indicates that the fault is on L1.
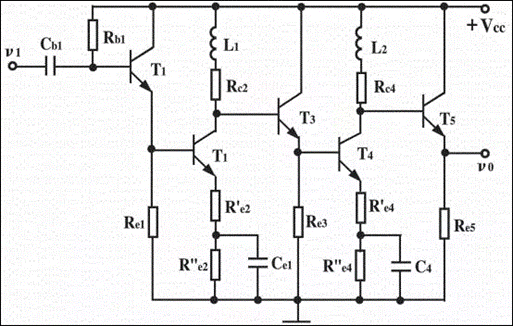
Amplification circuit for analyzing short circuit method
It should be noted that the short-circuit method can not be used in the power circuit. Remember.
Method 8: open circuit inspection method
The short circuit method mentioned above is very effective to check the open circuit. Similarly, it is also very effective to check the short circuit with the open circuit method. The thinking of open circuit inspection method is similar to the previous methods, which is used to eliminate doubts and shorten the scope. Suppose that the regulated power supply is connected to a faulty circuit, and the output circuit is too large at this time, then we disconnect some branches of the circuit in turn, and then observe the current output of the circuit, so as to judge the branch where the fault occurs.
In fact, the eight methods of appeal are just some commonly used methods. There are a variety of methods to judge faults. They can be flexibly applied through different instruments and equipment, so it will be easier to judge complex faults.
|
Disclaimer: This article is transferred from other platforms and does not represent the views and positions of this site. If there is infringement or objection, please contact us to delete. thank you! |











